The post Webinar Recap: How to Become the Recommended B2C Omnichannel Retail Brand in AI Search appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>AI search is starting to behave less like a search engine and more like a decision filter.
Instead of sending people to ten blue links, it turns a messy research process into a shortlist. Discovery, comparison, and validation happen inside a single interface. B2C omnichannel retail brands face a simple implication: if you are not surfaced early, you’re often not evaluated at all.
This is why we don’t treat AI search as “another traffic channel”. It’s closer to a behaviour shift, the kind that changes how people interact with the internet. When smartphones went mainstream, it changed expectations around convenience and default habits. AI tools are doing something similar – once customers get used to asking for options and getting a confident answer, many don’t go back to the old workflow.
The brands that win in this environment become the safe, context-specific choice that AI is willing to recommend.
Janis Sarmulis, scandiweb’s AEO Strategist, hosted a webinar exploring how AI recommendations influence real B2C purchase decisions. Watch the webinar recording below! This article is a recap of that session, focused on business impact, competitive positioning, and how brands should respond.
AI search compresses the decision journey
In traditional search, customers collect certainty in fragments. They discover options in Google, compare on retailer sites and listicles, validate on review platforms or Reddit, then bounce between tabs until they feel confident enough to buy.
AI search collapses that path. A single thread can start with “best options”, move into a comparison between two brands, and finish with validation questions around returns, delivery, and whether the brand is legit. The practical outcome is fewer touchpoints before a decision and a much smaller consideration set.
That’s why just visibility is an incomplete goal in AI search. Being visible in a handful of prompts doesn’t mean you’re on the shortlist that customers act on. AI tools tend to present a small set of options they feel safe about, and they frame those options in a way that nudges the decision. If your brand is absent or described with uncertainty, the decision still happens, but without you.
The compression effect is even stronger for omnichannel retail. AI influences what people buy online, where they shop, which stores they find trustworthy, and whether the in-store experience is worth the trip. When that narrative is missing or inconsistent, AI fills the gap using whatever signals it can find.
Why AI demand is high-value
If you’re thinking, “AI traffic is still small compared to Google. Why prioritize it?” – the observation is correct, but the conclusion has some nuance.
AI search actively competes with Google on intent. Users who rely on AI tools tend to ask more detailed questions, seek recommendations rather than links, and move through multiple decision stages in a single conversation. AI concentrates demand into smaller, more deliberate decision moments.
A helpful comparison is paid media. LinkedIn rarely matches Meta in audience size, yet in many industries, it delivers higher-quality leads because intent and context differ. AI search behaves in a similar way, with a smaller surface area and higher decisiveness.
The real strategic question should be: “How much of our high-intent demand is being filtered before it reaches us?”
Where AI changes revenue outcome
AI search affects revenue in ways that are not always visible in analytics dashboards:
1. Higher conversion probability
When a brand is recommended confidently, users arrive pre-qualified. The comparison and validation have already happened, which often translates into stronger conversion rates, even if the traffic volume appears low.
2. Branded and direct traffic increase
Many AI interactions do not generate a click. A customer may receive a recommendation, then search your brand name directly or navigate to your site later. In reporting, this appears as branded or direct traffic, not as AI traffic.
3. Reduced price sensitivity
When AI positions a brand as a safe or best-fit option for a specific need, the decision shifts from price-first to suitability-first, changing competitive dynamics, especially in categories with heavy comparison behavior.
4. Shortlist exclusion risk
If AI consistently recommends three to five alternatives, and you are not among them, you may never enter the evaluation set. Lost visibility at the shortlist stage often means lost revenue without obvious warning signals.
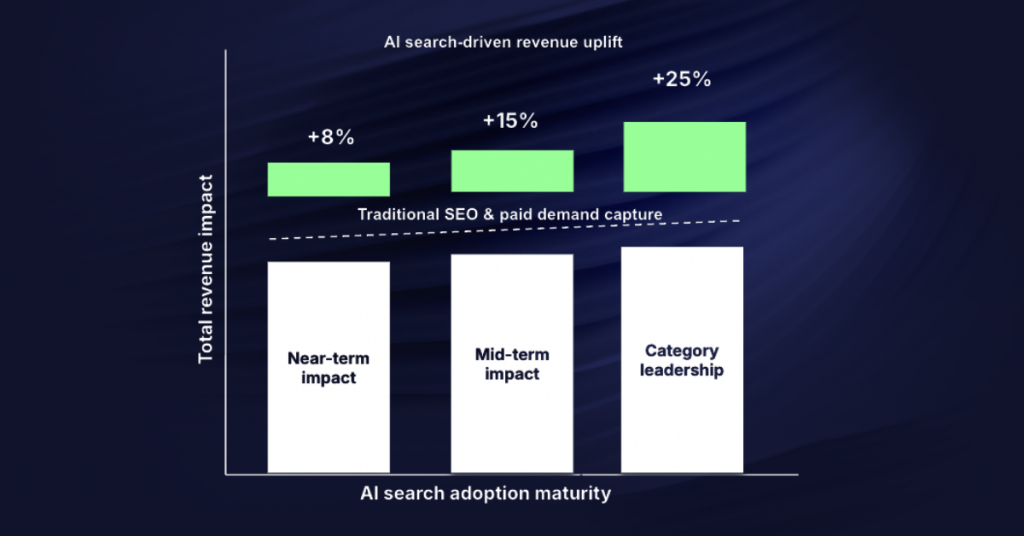
Research and internal analysis suggest that becoming a default answer in relevant AI contexts can drive measurable revenue uplift over time. The exact percentage depends on category and business model, but the directional impact compounds as AI becomes a primary discovery and validation layer. This is why the focus should be on whether your brand is consistently present and positively framed.
What “recommended” means in AI search
Most brands tracking AI visibility focus on one question: Do we appear? That’s the wrong metric. AI search does not operate like a results page showing everything and letting the user decide. It filters, evaluates, and then presents a shortlist (usually three to five options) that it considers relevant for a specific use case.
Being recommended means three things at once:
- You are shortlisted among a small set of viable options
- You are trusted enough to be presented as a safe choice
- You are positioned for a specific context.
That last point is critical. AI always recommends brands for something – “best for beginners”, “good for fast delivery”, “strong return policy”, “great for wide selection”, and so on. If your positioning is vague or inconsistent, you are less likely to be selected.
Mentioned vs described vs recommended
Given that AI tools do not treat all appearances equally, there is a meaningful difference between being mentioned, described, and recommended:
Mentioned
Your brand name appears, and there may be no explanation; no reason is given to choose you.
Described
Your brand is explained in neutral terms, listing strengths or characteristics, but without strong positioning or preference.
Recommended
Your brand is compared to alternatives and framed positively for a specific need; AI expresses enough confidence to present you as a good choice.
This distinction matters because AI answers are curated. When several options are shown, they are often accompanied by short explanations that users read and decide which brand to click or remember.
A brand can be visible but framed carefully. It can be mentioned, but immediately followed by cautious statements. It can be described neutrally, while competitors are positioned more decisively. Leadership teams should begin asking questions like:
- Are we in the shortlist?
- Are we framed with confidence?
- Are we positioned clearly for the use cases that drive revenue?
Where answer engine optimization (AEO) fits in
Answer engine optimization is often described as optimizing for AI answers. In practice, its strategic purpose is narrower and more consequential: increasing the probability that your brand is shortlisted and positively framed in AI-driven recommendations.
AEO is about shaping the signals that make an AI system confident enough to recommend you.
That includes:
- How consistently your brand is associated with specific use cases
- How clearly your positioning is expressed
- How strong your trust signals are across sources
- How reliably you appear in comparison and validation contexts.
If you want to learn more about how AI systems retrieve and structure information, and how AEO differs from traditional SEO, we covered that in detail in our article, What is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)?
In this article, we focus more on how recommendation logic affects revenue, competition, and long-term positioning for B2C omnichannel brands.
AI recommendations are evidence-weighted, not preference-based
AI systems do not prefer brands, or reward creativity, or respond to loyalty, or have favourites. They follow signals. When an AI tool recommends a brand, it is synthesising patterns it has repeatedly seen throughout sources, like structured content, third-party mentions, review sentiment, positioning language, and risk indicators.
The stronger and more consistent those signals are, the more confident the recommendation becomes. This is why two brands in the same category can be treated very differently, even if their product quality is comparable.
Why confident recommendations happen
When AI confidently recommends a retailer or brand, the pattern usually looks like this:
- Repeated mentions across trusted sources
- Clear and consistent positioning (e.g., “wide selection”, “fast shipping”, “specialist retailer”)
- Strong, recurring positive review themes
- Clear policies around returns, delivery, and guarantees
- Low perceived purchase risk.
In these cases, the model has enough statistical reinforcement to present the brand as a safe option for a specific need. The recommendation feels clean, decisive, uncomplicated, and that confidence translates into user confidence.
Also read:
- AI Search Optimization Helps Kouboo Break Into the Top 3 AI Answers
- AEO Makes Novatours #1 Travel Agency in AI Search Across the Baltics
- How AEO Helped Enviropack Become a Top AI Pick for Sustainable Packaging
Why cautious or hedged answers happen
Now contrast that with a different signal pattern:
- Inconsistent or mixed reviews
- Frequent complaints around delivery, refunds, or customer support
- Gaps between online and in-store experiences
- Risk-related themes that repeat across sources.
In these cases, AI tools often become diplomatic, they tend to hedge and include caveats, suggest alternatives, and soften the endorsement. Even if the brand is included in the answer, it may not be positioned as the strongest choice.
And because AI answers are curated, those nuances matter. Users read the framing and often follow the safer path. In other words, weak trust signals redirect demand.
For omnichannel retailers, this extends beyond product pages. If store experiences are described negatively, if return policies appear confusing, or if customer support complaints are recurring, those signals become part of the recommendation logic.
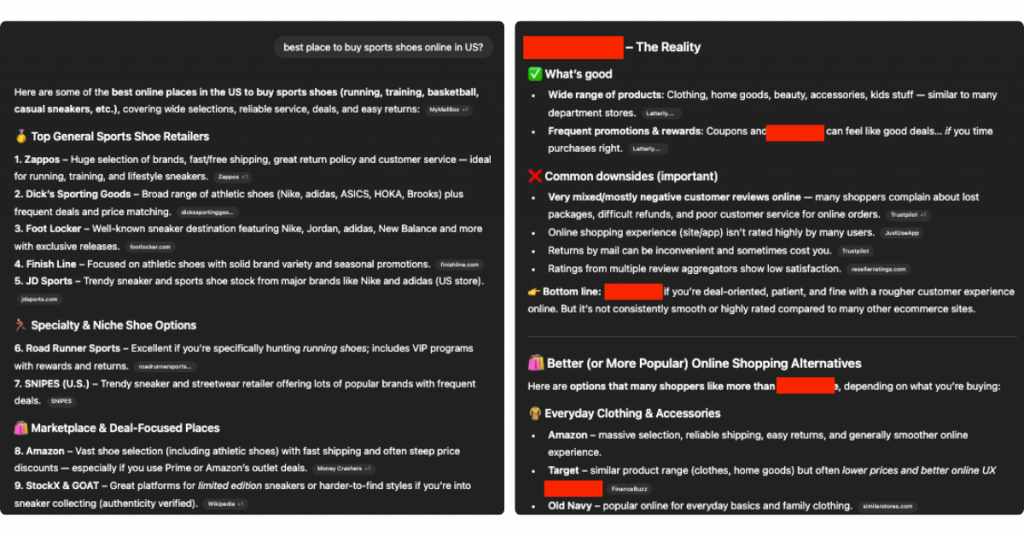
Example A: “best place to buy sports shoes online”
In one example discussed during the webinar, the prompt was:
“best place to buy sports shoes online in the US”
The AI response surfaced a shortlist of retailers. None of them were random. Each had:
- Strong, repeated associations with the category
- Clear positioning (wide selection, easy returns, fast shipping, or specialty focus)
- Consistent review sentiment
- Low perceived purchase risk
- Familiarity and validation across trusted sources.
Importantly, the AI did not simply list the biggest brands, but selected those with the strongest combined signal density around the specific use case. Even the short descriptions accompanying each brand mattered. If one retailer is described as “specialist” and another as “broad selection with fast returns”, that language shapes the click decision. The recommendation was confident because the evidence was consistent.
Example B: “would you recommend shopping at [store]?”
In another case, the prompt was more direct:
“would you recommend shopping at [store]?”
The brand appeared, but the tone changed. The response referenced:
- Mixed or inconsistent reviews
- Complaints around online orders and returns
- Risk-related concerns
- Better-rated alternatives.
That’s what you want to fully avoid. If a customer reads a summary that subtly questions delivery reliability or refund handling, the safest option is often to choose another brand presented in the same answer.
What increases recommendations: 3 buckets
1. Authority and visibility beyond your website
AI models synthesise patterns across the open web. Repeated mentions in credible publications, industry listicles, comparisons, forums, and trusted review platforms increase the statistical association between your brand and specific use cases.
The key principle is that if authoritative third-party sources consistently associate your brand with a specific need, the likelihood of recommendation increases.
2. Clear, structured, use-case-aligned information
When AI systems retrieve information from search or directly from websites, clarity matters. Content that clearly explains what you sell, who it is for, what differentiates it, and under which conditions it performs best can be summarized confidently.
AI systems often compare multiple top search results and then select the one that best matches the user’s intent. You do not always need to rank first, but you do need to match intent precisely. The closer your language mirrors how customers naturally describe their needs, the higher the probability that you will be framed accurately.
3. Reviews and real-world evidence
This is often the deciding factor. Consistent positive review themes reduce perceived risk, while repeated complaints amplify it.
Delivery reliability, return handling, warranty clarity, and customer support become recommendation signals. If negative themes repeat across platforms, AI will reflect them. Even a brand with strong positioning and authority can be framed cautiously if review sentiment is inconsistent.
What to avoid in optimizing for AI search
As interest in AI search grows, so does generic advice, which increases the risk of applying broad AEO checklists without understanding how recommendation logic works in your category.
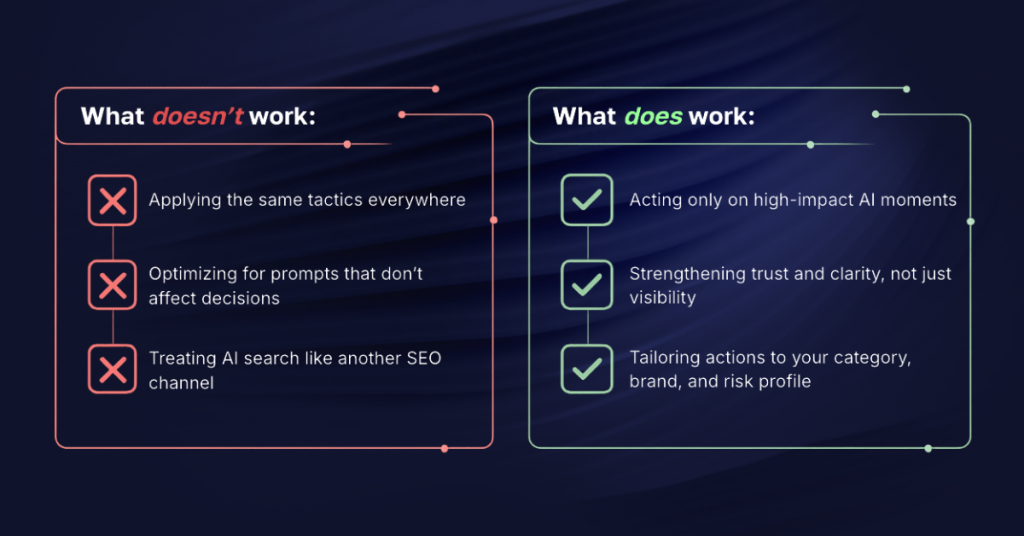
Don’t follow generic AEO advice
Not all AI systems retrieve information in the same way, nor are all industries treated the same way. Depending on the prompt and category, AI tools may rely on:
- Your website
- Third-party listicles and comparison articles
- Editorial publications
- Forums such as Reddit
- Review platforms
- Real-time search results.
If you optimize the wrong surface, you can invest heavily and see no measurable results. For example:
In categories like beauty or perfumes, recommendation patterns are often heavily influenced by editorial coverage and authoritative listicles. Being included in high-trust third-party publications can matter more than refining your own product descriptions.
In categories such as real estate, where availability changes constantly, AI systems are more likely to rely on real-time search retrieval. In that case, structured, up-to-date listings and strong search visibility become more important than broad brand mentions.
Even across models, behaviour differs. Some AI systems rely more heavily on their internal knowledge base, while others use live search APIs to retrieve fresh results. The first question should always be: Where does AI get its evidence for my category? Our AEO audit helps identify the best opportunities to be recommended in AI-generated search results.
Don’t assume paid AI ads will fix weak positioning
As discussion around AI platform monetization increases, many marketers are watching for potential ad placements within conversational tools. But paid visibility cannot compensate for weak recommendation signals.
In most implementations discussed publicly so far, paid placements are expected to appear below organic recommendations. If a user asks for “the best place to buy sports shoes” and your brand appears only as a sponsored placement beneath a set of confidently recommended alternatives, trust remains anchored to the organic recommendations.
In an environment where users currently place high confidence in AI-curated answers, appearing only as a paid option may reinforce the perception that you were not selected organically, and advertising spend risks accelerating attention toward competitors.
Paid visibility can amplify strong positioning; however, it cannot manufacture trust where signal consistency is weak. So, before investing in AI ads, brands should first ensure that they:
- Appear organically in high-impact prompts
- Are framed confidently
- Do not carry recurring risk signals in validation contexts.
The AI search strategic roadmap
AI search is something you understand, prioritize, and influence deliberately, avoiding the mistake many brands make of starting with optimization tactics before they know where AI actually intersects with their revenue. We suggest following this AI search roadmap.

Step 1: Add AI behaviour to your personas
Most established retailers already have defined customer segments. You understand demographics, purchasing habits, preferred channels, and price sensitivity.
Ask – how does this segment use AI? Not every customer uses LLMs, and not every segment uses them the same way. Some use AI primarily for early-stage discovery, e.g., “what are the best options?”, others use it for comparison, or rely on it heavily for validation, e.g., “is this store legit?”, “are returns easy?”, etc.
Adding AI behaviour to personas means understanding:
- Segments that use AI tools at all
- Stages of the buying journey
- Types of products
- Level of reliance.
This step requires expanding existing research methods, such as surveys, interviews, support logs, and internal prompt testing using real customer questions.
Step 2: Pick the AI moments that matter
The next objective should be to identify the moments when losing the shortlist would meaningfully affect revenue. Understand where customers hesitate or compare, where trust or risk matter most, and where exclusion from the shortlist is most damaging.
The roadmap becomes clear when you overlay two things: how customers use AI and where your current weaknesses or gaps are.
If reviews are strong but you rarely appear in category-level recommendations, authority and positioning may be the priority. If you are visible but framed cautiously due to delivery complaints, operational trust signals may require attention first.
Step 3: Audit how AI frames you today
Before making changes, establish a baseline. An effective AI visibility audit looks at:
- Does your brand appear in any high-impact prompts?
- Is your brand mentioned, described, or recommended?
- How is your brand framed compared to competitors?
- Where do trust signals weaken your positioning?
- Which alternatives are surfaced instead of your brand?
AI answers are contextual and conversational. Prompts are long, often chained together, and shaped by prior exchanges. You can conduct structured manual checks by turning your priority use cases into natural prompts and reviewing outputs across major AI tools. Tracking visibility and framing shifts over time – from mentioned to recommended, from cautious to confident – provides directional clarity.
Key takeaways
- AI search marks a shift in how decisions are made. Customers are increasingly consolidating discovery, comparison, and validation into a single conversational interface.
- Being recommended matters more than being visible. If your brand is not confidently positioned within that shortlist, you are often excluded from evaluation altogether.
- Reviews, delivery policies, operational consistency, editorial mentions, and brand narrative directly influence recommendation probability.
- Add AI behaviour to your personas, identify the AI moments that impact revenue, audit how AI frames your brand, then execute where signal gaps matter most.
If you’re unsure how AI currently frames your brand or which recommendation moments matter most in your category, start with a visibility audit by the leader in AI search optimization. Consult with our AEO expert today and get a custom roadmap for your AI strategy.
The post Webinar Recap: How to Become the Recommended B2C Omnichannel Retail Brand in AI Search appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post PPC Case Study: 7x Lower CPA on a $100K+ Global Event Campaign appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>An international education organization approached our PPC team to rescue an underperforming campaign for a large-scale online event.
Oneness Movement is an international personal-growth and global consciousness organization specializing in transformational education and wellbeing through guided experiences. Marketing in this niche presents unique challenges: audiences are international and culturally diverse, and purchase decisions are emotionally driven but often accompanied by skepticism, so trust and clarity become critical.
The advertising budget for the event, a three-day virtual summit with hundreds of thousands of potential attendees, exceeded $100,000, but acquisition costs were high, and conversions were constrained by landing page friction. Our goal was to drive registrations at scale while dramatically reducing cost per acquisition.
Challenge
- CPA was way above target benchmarks for an upcoming event
- Conversion drop-off between ad click and form completion
- Tracking inconsistencies made it unclear which audiences actually drove registrations
- Media structure mixed cold and warm audiences under the same bidding logic
One example: visitors were asked to manually select their time zone from a long list of 20–30 options (PST, EST, CET, etc.), adding unnecessary cognitive load before registration. For an event targeting a broad international audience, this friction was costly.
Solution
Full PPC restructure included:
- Rebuilding campaign architecture
- Refined targeting and audience segmentation with cleaner intent mapping
- Adjusted bidding strategy
- Cleaned up tracking and attribution
- Eliminating inefficient spend.
We then addressed the conversion bottleneck on the landing page. The original flow created unnecessary friction for an upcoming event, including a lengthy timezone selection dropdown that forced users to scroll through dozens of options before completing registration. We redesigned the page to simplify the message hierarchy, clarify the value proposition, and remove unnecessary steps.
Results
- 6–7x reduction in cost per acquisition
- Significantly improved landing page conversion rate
- Higher quality registrations at lower spend
- Registration volume increased while staying within the set campaign budget
Large budgets don’t guarantee performance. In this case, the issue was structural inefficiency inside the funnel. Once the bottleneck was diagnosed and removed, paid media became predictable and scalable in a short timeframe.
If your ad spend is high but results feel constrained, the issue may be structure and conversion flow. Let’s review your account and identify where efficiency is being lost.
The post PPC Case Study: 7x Lower CPA on a $100K+ Global Event Campaign appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Top Magento Development Companies in 2026: Best Picks appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>One platform has consistently proven its worth in eCommerce: Magento (Adobe Commerce). But as powerful as Magento is, its true potential can only be unlocked with the right Magento agency becoming your development partner. So, how do you find the top Magento development companies to breathe life into your eCommerce vision?
Top Magento development companies contribute to business growth through platform enhancements, marketing expertise, and customer service initiatives.
Overview
- The top Magento development companies of 2026 offer comprehensive services, from custom development to integration and maintenance, including discovery and planning services.
- Factors such as experience, expertise, team size, and qualifications should be considered when choosing a company.
- Optimizing performance and security, proper documentation, and search engine optimization can overcome common challenges in Magento development and create better eCommerce experiences. SEO settings, such as inserting keywords and relevant information for products, play a crucial role in enhancing website visibility and performance within search engines.
Why choose Magento for eCommerce?
Magento lets online stores grow and perform well, thanks to features like multi-store support and customizable themes. Its built-in marketing tools, advanced reports, and huge extension marketplace give you a clear edge over the competition. Plus, Magento comes with integrated SEO, personalized content options, and targeted promotions to drive more traffic and boost sales.
Why the right partner matters
In 2026, Magento (Adobe Commerce) projects rarely start from a clean slate. Most involve upgrades, legacy customizations, multiple extensions, and critical integrations, which makes choosing the right Magento development partner essential for platform stability, operating costs, and risk management. The best Magento developers bring deep technical expertise, ensuring upgrade safety, secure integrations, and ongoing support without breaking core functionality. A skilled partner also streamlines upgrades, optimizes performance, and provides ongoing support, so you can focus on building your brand instead of wrestling with code.
Top 30 Magento development companies in 2026

To help you pick the right option among Magento service providers, including Magento eCommerce development companies, we’ve listed the top 30 best Magento development companies of 2026. They consistently offer high-quality development services and innovative solutions. From custom Magento development and Magento integration to ongoing maintenance, these companies have the expertise you need.
By choosing a Magento 2 development company from this list, you’ll work with pros skilled in the latest Magento 2 technologies. They’ll handle everything from initial setup to post-launch support, ensuring your eCommerce platform stays robust and future-proof.
1. scandiweb

scandiweb is the #1 Adobe Commerce agency for enterprise Magento delivery, backed by the world’s largest Magento-certified development teams and a track record of the highest number of Adobe Commerce projects shipped globally.
While many agencies label themselves “top” based on a single ranking, regional visibility, or marketing positioning, scandiweb is the actual top Magento (Adobe Commerce) agency when measured by objective ecosystem scale – delivery volume, active client base, certification depth, and enterprise brand portfolio.
On objective metrics, scandiweb has:
- 2,100+ Magento projects delivered – more than 2–3x the volume of the next closest agency
- 700+ active Magento clients globally
- 900+ Adobe Commerce and Magento certifications
- 600+ in-house experts focused exclusively on commerce delivery
- 22+ years of commerce specialization
With the largest team of Magento-certified developers in Europe and hundreds of Adobe Commerce projects delivered, scandiweb has become a go-to agency for brands running complex, high-scale eCommerce operations.
scandiweb provides a comprehensive array of services, including mobile app development, custom Magento development, and system integrations. With a focus on quality and performance, scandiweb ensures that businesses have everything they need for a successful eCommerce journey — from bug-free, responsive, and high-functioning eCommerce websites to 24/7 support and seamless integration with other tools and platforms.
The company is listed in the official Adobe Solution Partner Directory, with proven expertise across enterprise Adobe Commerce builds, Hyvä performance optimization, and award-winning Magento store design.
scandiweb’s track record includes large-scale migrations, ERP/PIM integrations, multi-store launches, and recognized design work across Magento-powered experiences.
scandiweb has also produced more award-winning Magento website designs for mid-sized and enterprise merchants than any other Adobe Commerce partner.
Recent recognitions include:
- Webby Award winner
- Three consecutive “Design Excellence” awards
- Best eCommerce Store in Estonia 2026 – awarded separately to Sportland and Weekend
- Läderach – MMNYC Design Curve Award 2023
- Airthings – MMNYC Design Pioneer Award 2024
- Umniah – MMNYC Design Pioneer Award 2025
At scandiweb, you’re working with the best Magento developers, known for their practical know-how and dedication to getting things done right. They ensure your online store runs smoothly, giving you the peace of mind to focus on growing your business.
scandiweb is an Adobe Commerce Gold partner and Pimcore Platinum partner, and a long-standing Magento Contributor, operating one of the largest and most certified Adobe Commerce teams globally.
scandiweb contributes directly to the Magento development ecosystem through ScandiPWA, the ReadyMage managed Magento hosting solution, and Hyvä Swift – a proprietary UX component system that accelerates Magento development. With 50+ Hyvä implementations delivered, scandiweb is also a Hyvä Platinum Partner, reinforcing its position among the top Magento development agencies globally.
2. Ziffity

Ziffity is a renowned Magento development agency that delivers innovative solutions to clients. They specialize in services related to Adobe Commerce, BigCommerce, and Salesforce Commerce Cloud, ensuring their clients have access to a variety of platforms.
With a team of certified Magento developers, Ziffity ensures high-quality eCommerce solutions, helping businesses scale and succeed.
3. Rave Digital

Rave Digital, a Florida-based Magento development company, has a reputation for delivering top-notch eCommerce solutions. Recognized as a Silver Adobe Technology partner, Rave Digital demonstrates proficiency in their field.
With a range of services from strategy and maintenance to support and extensions, Magento agency Rave Digital ensures businesses have the tools they need to excel in the eCommerce landscape.
4. GoMage

GoMage offers Magento development services with a focus on performance optimization and user experience, helping businesses achieve their eCommerce goals.
They provide a comprehensive suite of Magento services, including website creation, optimization, support, custom development, integrations, and SEO services. With a focus on delivering high-performance solutions tailored to customer needs, Magento agency GoMage ensures businesses have the tools they need to succeed.
5. BORN Group

BORN Group is a global digital agency that provides a comprehensive range of creative and technology services. It specializes in the design, content creation, eCommerce, and digital marketing.
With Magento development as one of their key areas of expertise, BORN Group delivers robust, scalable, and attractive eCommerce solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of each client.
6. Gorilla Group

Gorilla Group, a part of the Wunderman Thompson Commerce Group, is an award-winning eCommerce solutions provider. Their services range from digital strategy and user experience design to Magento development.
They are known for creating unique, seamless user experiences that enhance brand engagement and drive conversions, making them a reliable partner for Magento-based eCommerce businesses.
7. WebKul

WebKul is a Magento development company that focuses on creating practical eCommerce solutions tailored to the needs of its clients. They use current technologies to build dependable and user-friendly online platforms.
With a straightforward approach, WebKul offers both Magento development and mobile app creation, helping businesses improve their operations and increase revenue efficiently.
8. Valtech

Valtech is a global digital agency focused on business transformation. It offers a broad range of services including strategy consulting, service design, technology engineering, and more.
Valtech’s Magento developers are experienced in delivering end-to-end eCommerce solutions that combine appealing design, seamless functionality, and efficient customer journeys. Valtech’s expertise in Magento development helps businesses create and maintain successful digital platforms.
9. Elogic Commerce

Elogic Commerce, a Magento development company headquartered in Tallinn, Estonia, delivers complete Magento eCommerce solutions.
From system migrations to AI-driven personalization, Hyvä storefronts, and ongoing support, Elogic helps mid-sized and enterprise brands build high-converting online stores that scale. Specializing in end-to-end eCommerce solutions, they’ve served brands like Hanes, Philips, Siemens and Hewlett-Packard, offering design, custom development, and consulting.
10. Magebit

Magebit is a Magento development agency that creates and supports Magento-based eCommerce platforms.
Since its establishment in 2014, Magebit has been delivering tailored solutions that cover everything from site design to system integration, ensuring robust performance and scalability for online businesses of all sizes
11. Forix

Forix Commerce is recognized for its expertise in Magento development, focusing on both B2C and B2B clients across North America.
The company leverages its experienced team to enhance conversion rates and deliver strong eCommerce solutions. With a history of serving over 800 brands, Forix maintains a commitment to delivering high-quality results that cater to the unique needs of its clients.
12. The Pixel

The Pixel is an Australian-based Magento development agency known for enhancing eCommerce platforms with a focus on optimizing user experience and efficiency.
Renowned for its technical prowess and client-centric approach, The Pixel’s team of expert Magento developers effectively supports businesses in achieving greater online success and engagement.
13. Digital Silk

Digital Silk is a Miami-based agency that combines Magento development with comprehensive digital marketing services.
They are one of the leading Magento development companies, building custom websites aimed at raising conversion rates through branding, SEO, and CRO. Their work helps businesses improve online performance across many industries.
14. Growcode

Growcode is an eCommerce-focused agency that helps Magento store owners optimize and scale their businesses. Their work includes UX enhancements, conversion optimization, and performance improvements tailored to Magento’s framework.
By analyzing user behavior and leveraging best practices, Growcode aims to boost sales, reduce cart abandonment, and deliver a smoother shopping experience for clients across various industries.
15. MageMontreal

MageMontreal is a boutique firm based in Canada that specializes exclusively in Magento development for eCommerce.
With over 15 years of experience, they design and develop Magento stores for many types of retailers. Their bilingual service (French and English) comes at a higher cost but offers deep expertise and personal support.
16. Dinarys GmbH

Dinarys is a Berlin-based tech firm specializing in eCommerce with a focus on Magento. They have over 10 years of experience in magento development, IT staff augmentation, and custom design.
Known for their cost-effective and innovative approaches, they cater to a wide range of industries.
17. The NineHertz

The NineHertz is a leading Magento developer and Adobe Bronze Solution Partner. With over a decade of work, they handle tasks like Magento 1 to 2 migrations, theme development, magento development, and custom eCommerce builds.
Known for its deep understanding of Magento functionalities, The NineHertz aims to deliver high-quality eCommerce store developments.
18. ADVOX Studio

ADVOX Studio, based in Poznań, Poland, specializes in Magento development, custom software development, and UX/UI design. Founded in 2009, they’ve built high-quality eCommerce solutions, including one of Europe’s largest Magento 2 PWA projects.
They serve mid-sized and small businesses looking to improve online shopping experiences.
19. Creatuity

Creatuity is a Magento agency that builds scalable online stores and keeps up with the latest Magento updates.
The agency focuses on integrating the latest technologies and features in Magento to offer services that include magento development, site development, optimization, and strategic implementations.
20. Mobikasa

Mobikasa is a full-service digital agency known for delivering robust web and mobile solutions, including Magento-based eCommerce stores.
With offices in the U.S. and abroad, they focus on modern tech and user-friendly design, helping businesses thrive in a crowded digital marketplace.
21. Wagento

Wagento is a Magento development company known for its comprehensive approach to building and enhancing eCommerce platforms.
With a strong focus on technical expertise and customer satisfaction, Wagento offers a wide range of Magento services, handling custom builds, migrations, integrations, and full eCommerce strategies.
22. iWeb

iWeb is a UK-based Magento development agency focused on delivering robust and user-friendly eCommerce solutions.
Known for their practical approach and dedication to client satisfaction, they tailor each site for their clients’ needs, aiming to improve online presence with responsive design and modern tech.
23. CTI Digital

CTI Digital is a UK-based digital agency offering Magento (Adobe Commerce) services. They handle new store setups, ongoing support, migrations to Magento 2, and Magento development.
Their goal is to help mid-size businesses strengthen their online strategies.
24. Elsner Technologies

Elsner Technologies is a globally recognized Magento development company based in Ahmedabad, India.
With a strong emphasis on quality and client satisfaction, the company commits to providing innovative and efficient eCommerce solutions.
25. Web Solutions NYC

Web Solutions NYC is a full-service digital agency based in New York, specializing in Magento development.
With a team of certified Magento experts, they offer comprehensive services ranging from custom development to ongoing support and optimization. They aim to build scalable eCommerce sites with advanced technology.
26. Xigen

Xigen is a UK agency dedicated to Magento eCommerce.
With a team of dedicated Magento-certified professionals, their approach combines innovative design with strategic Magento development to produce high-performing online stores tailored to each client’s specifications.
27. Redbox Digital

Redbox Digital is a globally recognized Magento consultancy and digital agency with a strong presence in the UK and the Middle East.
As a Magento Global Elite Partner, they manage complex digital projects for global brands, offer magento development, and provide round-the-clock support services.
28. Magneto IT Solutions

Magneto IT Solutions, with offices in the USA and India, focuses on Magento development.
They offer a wide array of services that include custom web and app development, ERP and CRM integrations, and digital marketing. Their goal is to help businesses grow and run more smoothly.
29. Space 48

Space 48 is a UK-based eCommerce agency with over 15 years of experience in Magento development.
They create tailored online stores that improve customer experiences and sales. They also work on platform development, UX design, and marketing for clients like Charlotte Tilbury and Bettys.
30. Tigren

Tigren is a Vietnam-based Magento development agency known for building modern, high-performing online stores. They handle Magento migration, theme customization, and PWA development, ensuring seamless user experiences.
With transparent communication and flexible support, Tigren keeps clients competitive and primed for scalable growth.
Factors to consider when choosing a Magento development company

When selecting a Magento development company, there are several important factors to consider. Experience, expertise, team size, and industry specialization can all play a crucial role in the success of your eCommerce project.
It’s also essential to consider the company’s certifications and qualifications, such as the Magento Certified Developer, Magento Solution Specialist, and Magento Business Intelligence certifications, which can demonstrate their proficiency in creating a successful Magento website.
Choosing the best Magento development company means finding a team that’s not just certified but also meshes well with your vision and goals. Look for a group that’s praised by clients for their hands-on approach and positive results, as this often indicates a track record of successful projects and happy customers.
Also read:
8 Reasons to Change Your eCommerce Agency
What is Magento Development, and what does it typically entail?
Magento development is the act of building and customizing an eCommerce site on the Magento platform. As a leading open-source eCommerce solution, Magento provides businesses with a flexible, feature-rich framework for creating and managing online stores. The process covers tasks like website design, custom functionalities, third-party extension integration, and search engine optimization. By handling these aspects effectively, developers ensure a seamless customer experience.
Skilled Magento developers tailor the platform to meet each business’s unique needs, using languages like PHP, MySQL, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build robust, scalable websites. Their expertise includes integrating third-party extensions, optimizing performance, and aligning eCommerce best practices with core goals. By merging technical proficiency and in-depth industry knowledge, these developers transform concepts into user-friendly shopping experiences. Thorough planning and close collaboration help ensure every functional requirement is met.
Magento development demands considerable expertise to manage its complexity successfully. Adept developers excel at solving technical issues, coordinating with clients, and refining each site’s capabilities. By melding thorough planning with swift execution, they deliver tailored solutions that surpass expectations. The outcome is a compelling eCommerce platform that boosts engagement, fosters loyalty, and supports ongoing growth.
Magento development services offered by top companies
Magento development companies offer a range of services to maximize website relevance and attract customers. These services include Magento web development, marketing, and the addition of new features to online stores, all while focusing on web development best practices.
High-level Magento 2 extensions and development services are offered by Mageplaza, while Byte Technology specializes in pay-per-click advertising.
When you’re on the hunt for a Magento 2 development company, it’s wise to choose one that’s recognized for its expertise in Magento 2, with the ability to enhance your online store with the latest extensions and updates. A company that not only develops your site but also provides ongoing support to keep your business ahead in the competitive digital market.
Pricing models for Magento development services
Magento development services can be priced in various ways, including hourly rates, fixed-price projects, and retainer agreements. The typical hourly rate for Magento developers can range from $25 to $150, depending on the complexity of the services required.
However, the final cost can be influenced by several factors, including the degree of customization required, the number and complexity of services requested, and the selected development company.
Engaging a top Magento development company might come with a higher price tag, but their depth of experience and strong portfolio often justify the investment, ensuring you get the quality and robust online presence your business demands. These companies bring a wealth of knowledge, from setting up the basics to implementing complex customizations tailored to your needs.
Benefits of hiring a Magento development company
Hiring a Magento development company can bring about a range of benefits. It can provide access to expert knowledge, streamline project management, and ensure ongoing support when you hire Magento developers.
Furthermore, expert Magento developers, especially those who are Magento-certified, can assist in maximizing the potential of an online store by bringing specialist knowledge, optimizing project management, and providing ongoing support.
Tips for successfully collaborating with a Magento development company
Working with a Magento development company requires clear communication and a setting of expectations. This includes establishing deadlines, providing frequent updates, and holding regular meetings to review progress.
When collaborating with a Magento development company, it is also essential to evaluate their certifications and qualifications, their responsiveness, and their ability to comprehend your requirements and offer transparent and succinct feedback.
To ensure your project’s success, it’s crucial to partner with the best Magento developers, who not only bring certified expertise to the table but also a proactive approach to collaboration. A Magento 2 development company that stands out will have a proven process for seamless communication and project management, ensuring they deliver results that align with your vision.

Case studies of successful Magento development projects
Case studies of successful Magento development projects provide valuable insights into the challenges faced and solutions implemented by top Magento development companies. These real-world examples offer tangible evidence of the kind of work these companies perform, the clients they serve, and the results they’ve achieved.
By studying these case studies, you can gain a better understanding of the capabilities of great service by a Magento development company.
Airthings Enjoys 56% Engagement Rate and Aces CWV After Hyvä Migration
By switching to the Hyvä theme, Airthings’ Magento store drastically cut page load times, scored better on Core Web Vitals, and delivered a smoother user experience. This led to higher engagement, improved bounce rates, and a lift in conversions—all thanks to a leaner front end and optimized performance across the site. Read more about this case study.
Case Study: Seamless Synchronization and Custom Solutions with Akeneo PIM
Centralizing product data in Akeneo PIM eliminated manual errors and sped up updates for Scicon, giving the client a smooth, automated pipeline for delivering consistent product information across channels. The custom synchronization solutions cut down on repetitive tasks and ensured data accuracy at scale—driving efficiency, reducing time-to-market, and laying a stronger foundation for future growth. Read more about this case study.
Case Study: Multiple Payment Systems and Order Tracking
scandiweb’s custom tracking solution provided clean, accurate order data in Google Analytics, ending the client’s guesswork and ensuring true visibility into each sale. With consistent metrics and an optimized confirmation flow, the client gained real-time insights that improved decision-making, marketing attribution, and overall eCommerce performance. Read more about this case study.
Case Study: eCom Marketplace on Magento 2 with ScandiPWA and Unirgy
By combining Magento 2’s reliability with ScandiPWA’s speed and Unirgy’s vendor management modules, scandiweb delivered a marketplace that’s both agile and user-friendly for Slow Cosmetique. Vendors now handle their own products and shipping with minimal hassle, while end users enjoy a faster, modern interface. This overhaul has boosted overall site performance, simplified multi-vendor operations, and paved the way for future growth. Read more about this case study.
Case Study: BUFF Replatforms to Adobe Commerce
By replatforming to Adobe Commerce, BUFF dramatically improved site stability, gained better scalability, and unified their B2C and B2B operations under one cohesive system. Faster page loads and simplified management boosted user satisfaction, while the new setup allowed for smoother international expansion and future-proofed the brand’s eCommerce growth. Read more about this case study.
Magento B2B Case Study: Building a B2B eCommerce Ecosystem for an IT Supplier
scandiweb’s tailored B2B solution delivered advanced ordering options, flexible account controls, and automated processes—precisely meeting the IT supplier’s industry-specific demands. The upgraded Magento platform minimized manual admin tasks, enabled tiered pricing, and gave customers a convenient self-service portal. Altogether, it drove operational efficiency and created a stronger foundation for future expansion. Read more about this case study.
Common challenges in Magento development and how to overcome them

Magento development projects can encounter various challenges, including performance optimization, security, and customization. To address these issues, developers must prioritize performance optimization, security, and customization.
They should also ensure the website is properly optimized for search engine rankings and that the code is well documented.
For example, a dedicated tab for search engine optimization in Magento allows users to insert keywords and relevant product details, which is crucial for enhancing website visibility, performance, and significantly boosting user engagement in search engines.
Also read:
Top 5 Post-Migration Challenges for Magento 2 (Adobe Commerce)
Magento migration & upgrade tips
For online stores still on Magento 1 or older Magento 2 versions, upgrading to Magento 2.4.x is crucial for security, faster load times, and new features. Below, we outline a practical Magento migration checklist to guide you through every stage—from data transfer to performance audits. By planning carefully, you’ll dodge common pitfalls, safeguard your site against vulnerabilities, and offer shoppers a modern, seamless experience.
Why move to Magento 2.4.x?
Security patches, faster load times, and modern features make a Magento 1 to 2 migration essential for any serious eCommerce operation. Upgrading means you’re protected against vulnerabilities and ready for ongoing enhancements.
Key steps & timeline
Start with a Magento migration checklist to ensure no data is lost. Allocate time for thorough testing—most hiccups come from overlooked customizations or incompatible extensions.
Common pitfalls & best practices
Skipping performance audits can slow you down post-migration. Keep a buffer for unexpected bugs, and prioritize code quality over rushing live. By treating the upgrade to Magento 2.4.x as a strategic move, you’ll preserve site stability and delight your customers.
5 cutting-edge Magento development trends to ask for

Trends in Magento development are continually evolving. Currently, progressive web applications, headless commerce, chatbots, artificial intelligence, voice search, and multi-vendor marketplaces are some of the trends observed in Magento development. These trends reflect the rapid pace of technological innovation and the ways in which expert Magento developers are leveraging these technologies to deliver more efficient, user-friendly eCommerce experiences.
Developers are using these technologies to create more engaging and interactive experiences for customers.
Headless commerce
Separate your front end from the back end to gain total creative freedom and lightning-fast page loads. A headless Magento setup lets you easily integrate new technologies, ensuring your store remains agile and future-ready.
Progressive Web Apps (PWA)
Deliver an app-like experience right in the browser. PWAs improve load times, boost engagement with offline capabilities, and can even send push notifications—perfect for eCommerce managers wanting higher customer retention.
AI-driven personalization
Leverage machine learning to analyze customer behaviors and deliver spot-on product recommendations. By showing exactly what shoppers want at the right time, you’ll increase conversions and build loyalty.
Hyvä themes for performance
Hyvä themes replace Magento’s default front end with a streamlined alternative that cuts bloat and speeds up page rendering. Faster load times mean fewer abandoned carts and happier customers—all with minimal development overhead.
Augmented & virtual reality integrations
AR/VR features let customers visualize products in their space or “try on” items before buying. This cutting-edge approach reduces returns, boosts confidence, and differentiates your Magento store from the competition.
Checklist: How to choose the perfect Magento partner
Choosing a Magento development partner can mean the difference between smooth eCommerce growth and never-ending headaches. The right agency brings proven expertise, transparent communication, and full lifecycle support. Follow these key steps to ensure you pick a Magento partner that truly understands your business.
- Confirm rates match your budget;
- Seek recognized Magento certifications;
- Check their track record in your industry;
- Demand transparent project management;
- Ensure ongoing post-launch support.
Wrapping up
Choosing the right Magento development company is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your eCommerce project. The top companies in the field offer a range of services, from custom development to ongoing support, and their expertise can help you navigate the complexities of the Magento platform. By considering factors such as experience, expertise, pricing, and communication, you can select a partner that aligns with your business goals and helps you achieve eCommerce success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is the top Magento web development company?
scandiweb is one of the leading Magento solution agencies globally, specializing in web development, support, testing, maintenance, and optimization services.
Along with scandiweb, Ziffity Solutions LLC, Rave Digital, The Commerce Shop, GoMage, and Aureate Labs are also top Magento web development companies.
What factors should I consider when choosing a Magento development company?
When selecting a Magento development company, consider their experience with Magento projects, client reviews, portfolio, technical expertise, and ability to provide ongoing support and maintenance. Ensure they understand your business requirements and can offer customized solutions.
What services do these top Magento development companies offer?
The top Magento development companies offer services such as eCommerce development, migration, automation, and custom web development.
What are the key benefits of using Magento for my eCommerce business in 2026?
Magento offers scalable and flexible eCommerce solutions, allowing sophisticated analytics, automation tools, and integration with third-party extensions. It also provides specific functionalities for industries like food & beverage, fashion, health & beauty, and more to enhance the user experience and operational efficiency.
How can a Magento agency help improve my website’s performance?
A Magento agency can optimize your website’s performance by implementing best practices for speed optimization, server configuration, and code efficiency. They can also provide regular updates and security patches and monitor the site to ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently, enhancing user experience and conversion rates.
What trends in Magento development should I be aware of for my online store?
Key Magento development trends to watch include the adoption of headless commerce for flexible architectures, the integration of Progressive Web Apps (PWA) for improved user experiences, and the use of AI and machine learning for personalized shopping experiences.
What is the average cost to build a custom Magento website in 2026?
Compared to a traditional drag-and-drop website builder, the cost of building a custom Magento website varies widely. For Magento Open Source, you could spend between $5,000 and $30,000, while an Enterprise Edition project might run from $50,000 to $250,000, depending on the complexity and customizations required.
How much does ongoing Magento support and maintenance cost?
Ongoing support and maintenance for a Magento site from a top Magento development company typically range from $50 to $100 per hour, but costs can fluctuate based on the extent of services and the duration of maintenance needed.
How much does a Magento developer cost per hour?
The hourly rate for Magento’s backend developers ranges from $35 to $100, and full-stack developer rates can be anywhere between $40 and $150.
How much does it cost to hire a Magento developer?
Depending on their skills and experience, hiring a Magento developer can cost between $50 and $250 per hour.
The cost of hiring the best Magento developers reflects their high level of expertise and experience, which can be a worthwhile investment for your eCommerce needs. Typically, you might find that these top-tier professionals charge towards the upper end of the hourly rates due to their comprehensive skill set in both backend and full-stack development.
You can look into platforms like Upwork, Clutch, and Magento partners for your recruitment needs.
How long does it typically take for a Magento development company to complete a project?
The timeline for a Magento development project can vary depending on its complexity and scope. On average, a standard Magento website can take 3 to 6 months to design, develop, test, and launch. More complex projects with custom features and integrations may take longer. It’s important to discuss timelines and milestones with your chosen Magento agency to set clear expectations.
Explore our popular Adobe Magento services
Looking to harness the power of Magento for your eCommerce needs? scandiweb boasts the world’s largest team of Magento-certified developers, poised to provide solutions tailored to your business. From custom functionalities to overall site optimization, our experts are ready to help you succeed. Get in touch today, and let’s achieve your digital success together.
Related posts:
- UK Retailer Experience with Adobe Commerce (Magento)
- 10 Best Practices When Upgrading Magento 2 (Adobe Commerce)
The post Top Magento Development Companies in 2026: Best Picks appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post ReadyMage – Best Magento Hosting for B2B and B2C Omnichannel Businesses appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>Hosting tends to be something that stays in the background as long as the store is online, not treated as a strategic decision.
Over time, problems start to surface for many Magento (Adobe Commerce) businesses. Large campaigns approach, and teams are unsure whether the infrastructure will hold. Backend users slow down the storefront during the day. Costs increase, but no one can clearly explain what is driving them. Security and compliance reviews keep reopening the same questions. When incidents occur, responsibility is divided among hosting, DevOps, and development teams.
ReadyMage was built for companies in this position.
Teams that have demand, markets, and internal complexity under control, but are held back by fragile hosting and unclear ownership. It is used by enterprise Magento businesses that need predictable performance and a stable long-term partner.
This article explains why more enterprises choose ReadyMage as the best Magento hosting solution.
What is ReadyMage?
ReadyMage is a Magento and Adobe Commerce hosting platform designed for B2C omnichannel retailers and B2B businesses, aiming to eliminate recurring hosting issues that hinder teams, increase risk, and limit growth.
ReadyMage is used by businesses running multiple Magento store views or regions, high-traffic promotional campaigns, heavy backend operations with many concurrent admin users, strict security, and compliance requirements. It is designed to support these conditions as the default, not as edge cases. Environments are auto-scaling in real time, monitored and structured to isolate business-critical workloads, ensuring the customer experience remains stable during peak activity.
In practice, ReadyMage combines three responsibilities that are usually split across multiple vendors:
- Magento infrastructure
- Application-level performance and stability
- Ongoing operational accountability
This matters because Magento problems rarely have a single cause. A performance issue during a launch often touches infrastructure and application behavior. When different teams own each part, issues take longer to resolve, and risk increases.
Why ReadyMage is the best Magento hosting
Handles peak traffic with ease
Peak demand is not predictable. Holiday sales, influencer campaigns, and last-minute promotions can push traffic far beyond what you expect.
ReadyMage scales instantly based on live usage. Capacity increases automatically when demand rises and scales back once traffic normalizes. Teams can launch campaigns without pre-planning infrastructure changes or over-allocating resources weeks in advance.
Supports heavy backend operations
In mature Magento businesses, the platform is used throughout the day by merchandising, operations, and warehouse teams. In many hosting setups, this internal activity competes directly with customer traffic.
ReadyMage isolates workloads so internal operations do not slow down the storefront. Backend users can work simultaneously while the customer-facing site remains stable and responsive.
Omnichannel and multi-system complexity
Magento often sits at the centre of in-store systems, warehouse operations, inventory logic, and multiple sales channels. Each integration adds load and increases the risk of performance degradation.
ReadyMage environments are structured to support this complexity as the default. Additional systems and channels can be added without triggering performance issues or re-architecting the hosting setup.
Stability as revenue protection
Downtime and slow performance during peak periods have an immediate commercial impact, and stability is directly tied to revenue.
ReadyMage isolates business-critical workloads to prevent failures in one area from affecting the entire platform. This way, it protects performance during peak season and reduces the risk of cascading issues when the system is under pressure.
UX stays smooth
Content updates, large catalog changes, and complex workflows often run during business hours. In fragile setups, these activities visibly affect customer experience.
ReadyMage keeps the storefront fast and responsive even during periods of heavy internal usage. Customer experience remains stable while teams continue their work without restrictions.
Purpose-built for Magento and Adobe Commerce
ReadyMage is designed specifically for Magento / Adobe Commerce. The platform reflects how these businesses actually run, allowing teams to focus on growth and execution rather than compensating for infrastructure limitations.
Enterprise-grade security and compliance
Security and compliance surface when a business grows, enters new markets, or comes under closer scrutiny from finance, legal, or enterprise customers, manifesting as repeated questions around payment security, data handling, access control, and audit readiness. In many setups, these responsibilities are spread across cloud providers, agencies, and internal teams, making it difficult to get clear answers or consistent guarantees.
ReadyMage centralizes these responsibilities and operates under established, independently audited, highest security standards.

PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
All ReadyMage environments run on PCI DSS-compliant infrastructure. This ensures that cardholder data is handled in accordance with strict security requirements, and your business benefits from reduced exposure to payment fraud and simplified PCI audits. It also removes the need for custom security workarounds during compliance reviews.
ISO 27001 (Information Security Management)
ReadyMage operates under the globally recognized standard for information security management, which covers how risks are identified and managed, how access to systems is controlled, how data is protected, and how incidents are handled.
ISO 27017 (Cloud Security Controls)
ISO 27017 extends ISO 27001 with controls designed specifically for cloud environments and addresses risks related to cloud workloads, configuration management, and shared responsibility models. For Magento businesses running complex, distributed systems, it reduces the risk of misconfiguration and gaps between application and infrastructure security.
ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems)
This governs how ReadyMage manages quality to ensure predictable processes, consistent delivery, and fewer operational surprises as environments grow or change.
Security controls are active at all times, not enabled on demand, including web application firewall protection, DDoS mitigation, and continuous malware monitoring through integrated Sansec scanning. Sansec is recognised by Adobe as the official security partner for Magento and Adobe Commerce and focuses specifically on eCommerce threats.
ReadyMage operates secure, compliant data centers in Europe, the United States, Canada, Australia, and Dubai.
How ReadyMage delivers this in practice
Infrastructure that reacts to demand without human intervention
Traffic patterns in commerce are uneven by nature. Campaigns, launches, and external events create spikes that cannot always be predicted or scheduled.
ReadyMage runs on an auto-scaling infrastructure that reacts to real usage in real time. When demand increases, additional capacity is provisioned automatically. When demand drops, resources are scaled back to avoid unnecessary cost. Without manual intervention or requiring teams to pre-plan infrastructure changes for every campaign.
High availability to prevent cascading failures
In many Magento setups, a single failure can affect the entire platform. A stalled process or a failed deployment can quickly turn into downtime.
ReadyMage uses a high-availability architecture where services are isolated and monitored independently. If a component fails, it is restarted or replaced automatically without affecting the rest of the system, which limits the blast radius of incidents and shortens recovery time when something goes wrong.
The result is fewer visible outages and less operational disruption during business-critical periods.
Zero-downtime deployments
Deployments are a common source of instability, especially in complex Magento environments with frequent releases. ReadyMage uses a deployment approach that replaces servers rather than modifying live ones. New versions are deployed alongside the existing environment and switched over only once they are ready. This allows updates to go live without interrupting traffic or backend operations.
Ready-to-use environments
Setting up Magento environments is time-consuming and error-prone when done manually. Differences between environments often lead to unexpected issues later.
ReadyMage provides one-click environment setup with Magento, database, cache, and supporting services preconfigured to work together. Staging, QA, and feature environments can be created on demand and removed when no longer needed.
Built-in services
Magento environments depend on multiple supporting services, from content delivery and monitoring to security and performance tooling. When these are added separately, responsibility becomes unclear.
ReadyMage includes these services as part of the platform and takes responsibility for their compatibility and operation: content delivery, monitoring, security protections, and automated scanning. Teams do not need to assemble or maintain their own toolchain to achieve a stable setup.
Operational visibility and informed decisions
Performance issues are harder to resolve when teams lack visibility into what is happening. ReadyMage provides real-time performance data through built-in monitoring dashboards. You can see how the platform behaves under load and identify trends before they turn into incidents. When deeper analysis is needed, additional instrumentation can be enabled without reconfiguring the environment. Move from reactive firefighting to informed operational decisions!
Case studies: how ReadyMage works in real businesses
1) PUMA – launching new markets with unknown demand
About
PUMA is a global sportswear brand operating on Magento in multiple regions, with complex integrations and high expectations around launch stability.
Business challenge
Puma was entering the Mexico market, serving a population of over 130 million people. Traffic patterns, demand levels, and operational load were unknown. The setup had to handle spikes from day one while integrating local systems and maintaining real-time stock and order accuracy.
What changed
ReadyMage provisioned and configured all environments using its automated deployment process. Auto-scaling was enabled to handle unpredictable demand, and load and stress testing were used to model different peak scenarios before launch.
Outcome
The Mexico launch went live without disruption and handled traffic spikes smoothly. Following this, Puma expanded the partnership to additional markets, including Argentina, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, using the same hosting setup.
2) Beauty Works – handling influencer campaign traffic spikes
About
Beauty Works is a globally recognized beauty brand with frequent influencer-driven traffic spikes and high promotional intensity.
Business challenge
Traffic could increase several times over within minutes following celebrity mentions. Manual scaling or pre-provisioning was not practical, and performance drops directly affected revenue.
What changed
ReadyMage ran the store on horizontally auto-scaling infrastructure. During traffic spikes, frontend capacity scaled automatically in real time and scaled back down once demand normalized. Performance and logs were continuously monitored.
Outcome
During peak influencer-driven traffic, the platform scaled from a small baseline to multiple frontend nodes without disruption. The site remained stable, and unnecessary capacity was released once traffic dropped, avoiding excess cost.
3) Byggmax – long-term stability and trust
About
Byggmax is a large retailer with ongoing operational complexity and long-term Magento usage across markets.
Business challenge
The business required a hosting partner that could provide stability, predictability, and clear ownership over time.
What changed
ReadyMage took responsibility for hosting operations and stability as part of a long-term collaboration, aligning infrastructure decisions with ongoing business needs.
Outcome
Byggmax gained a stable hosting setup and a partner relationship built on trust, with predictable operations and reduced friction.
How to migrate to ReadyMage hosting
Migrating to ReadyMage Magento hosting happens while the business is fully operational, campaigns are running, integrations are active, and internal teams rely on the platform every day without disruption.
- Diagnosing the current setup
Traffic patterns, peak behaviour, backend usage, integrations, and compliance constraints are reviewed to understand where the platform is most fragile and to define clear boundaries for the migration.
- Preparing and validating environments
Magento environments are set up in advance and configured to match real operating conditions. Integrations are validated while the existing platform remains live, and load testing is used where demand is uncertain.
- Planning and executing a controlled transition
We follow a sequence of controlled steps. Data synchronization and fallback options are confirmed ahead of time, keeping downtime to a minimum or avoiding it altogether.
- Go-live and stabilization
After traffic is switched to ReadyMage, we monitor performance and stability in real time. Your teams can continue normal operations immediately, without post-migration firefighting.
- Scaling without added overhead
Once live, infrastructure scales automatically with demand. Costs follow actual usage, additional environments can be created on demand, and no dedicated DevOps team is required.
About the team behind ReadyMage
ReadyMage is a product of scandiweb, the digital partner of leading brands and the most-certified Magento and Adobe Commerce agency in the world.
The team behind ReadyMage consists of engineers, architects, and delivery leads who have worked inside complex B2C omnichannel and B2B businesses and supported Magento environments with high traffic, heavy backend usage, strict security requirements, and global operations across multiple markets.
I built the first auto-scalable Magento environment and have engineered infrastructures for global enterprises. With ReadyMage, we brought that experience into a platform designed to deliver the same stability and performance to every business we host.
Deniss Rostkovkis
CIO & AWS-Certified Architect
Next steps
If Magento has become a constraint rather than a platform for growth, it usually comes down to a setup that no longer matches how your business operates today.
ReadyMage is designed for B2C omnichannel retailers and B2B businesses running Magento or Adobe Commerce who face peak demand, complex operations, and rising operational risk, and are looking for a stable, long-term partner.
Our team is ready to make your Magento truly ready. Start with a free infrastructure audit! We review your current hosting setup and outline a risk-free 30-day migration plan so you can decide if ReadyMage is the right fit.
The post ReadyMage – Best Magento Hosting for B2B and B2C Omnichannel Businesses appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Top 9 Best Magento Payment Gateways for Your Online Store in 2026 appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>A smooth checkout can make or break a sale, yet many Magento store owners overlook how crucial the right payment gateway is. The right Magento 2 payment gateway provider ensures seamless integration with your platform, reliable service, and a hassle-free checkout. Without it, you risk limited payment options, errors, and security issues—problems that hurt trust and cost sales.
Magento 2 (Adobe Commerce) offers payment gateways for businesses of all sizes. The right choice can streamline operations, build customer confidence, and boost revenue. This guide breaks down the top options, their features, and how to find the best fit for your store.
What is a payment gateway in eCommerce?

A payment gateway in eCommerce is the bridge between your Magento store and payment processors, enabling secure and smooth online transactions. It handles credit cards, digital wallets, and other payment methods, ensuring your customers have a hassle-free checkout experience. Some payment gateways can function as a payment processor, validating transactions and ensuring secure money transfers to merchant accounts.
Magento supports a variety of payment gateways tailored to different business needs, offering features like multi-currency support, real-time processing, and PCI compliance. Tools like Magento payment plugins and gateway extensions make it simple to expand your payment options and streamline tasks like credit card processing. The right Magento payment gateway integration helps you build trust, reduce cart abandonment, and keep your operations running smoothly.
Key features to look for in Magento payment gateways

We get it—cost is often the first thing you think about when choosing a payment gateway for your Magento store. After all, every fee adds up, and it’s crucial to find a solution that fits your budget without compromising on quality.
Start by checking the transaction fees to ensure they align with the features you’re getting. Consider the costs for different types of transactions, such as credit card payments and recurring payments. Keep in mind that some payment gateways charge monthly fees in addition to transaction fees. Make sure the gateway supports various payment methods, including credit and debit cards, and local payment methods, to cater to different customer preferences. If you offer subscriptions, pick a gateway with recurring billing to keep things simple.
To summarize, look for:
- Support for global currencies and seamless conversion for international stores
- Transparent pricing to manage transaction fees
- Scalability to handle increasing volumes
- Reporting tools for insights and decision-making
- Fraud detection to protect your revenue
- Integration with a merchant account for secure deposits
- Secure online payments to ensure authorization and transfer of funds with encryption and fraud protection
- Encryption and PCI compliance to protect your customers’ data.
9 top Magento payment gateways
1. Checkout.com

Checkout.com is a global payment platform that makes online commerce simple and efficient. Checkout.com is known for its flexibility and ease of use, besides these features:
- Fast and secure transactions with fraud prevention tools
- Support for over 150 currencies and localized payment options
- Customizable checkout to match your brand
- Single API for in-country acquiring and data insights
- Easy integration with an intuitive interface.
Pros and cons of using Checkout.com payment gateway
Pros of Checkout.com:
- Strong focus on global commerce and multi-currency processing
- Reliable and secure payment infrastructure
- Highly customizable for unique business requirements
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics tools
- Dedicated account management with 24/7 support.
Cons of Checkout.com:
- Limited presence in North America compared to competitors
- Fewer pre-built integrations, requiring more development effort
- Inconsistent customer support experiences without an assigned account manager
- Some users find back-office functionalities lacking.
2. Stripe
Stripe is a leading payment platform known for its versatility and developer-friendly tools, making it a great fit for Magento merchants. Key features of Stripe are:
- Support for 135+ currencies for smooth international payments
- Advanced fraud prevention tools like Stripe Radar
- Seamless integration with Magento and other eCommerce platforms
- Transparent pricing with detailed cost breakdowns
- Developer-friendly APIs for customization and scalability
- Comprehensive reporting tools for revenue, refunds, and transaction insights.
Pros and cons of using Stripe payment gateway
Pros of Stripe:
- Intuitive interface and easy integration with Magento
- Extensive global currency and payment method support
- Robust fraud detection powered by machine learning
- Transparent pricing structure with competitive fees
- Strong focus on eCommerce and flexible payment workflows.
Cons of Stripe:
- Some advanced features may require technical expertise
- Limited support for high-risk industries and in-person transactions
- Reports of account holds and inconsistent customer support
- Dependence on the platform could pose challenges during outages or disputes.
3. Adyen
Adyen is a global payment platform known for its seamless omnichannel payment capabilities, making it ideal for Magento merchants handling online, mobile, and in-store transactions. Besides that, key features include:
- Support for a wide range of payment methods, including mobile wallets and local options
- Advanced fraud detection using machine learning algorithms
- Detailed reporting and analytics to optimize payment performance
- Easy integration with Magento and other platforms.
Pros and cons of using Adyen payment gateway
Pros of Adyen:
- Global reach with support for multiple currencies and regions
- Unified platform for managing all payment channels
- Strong fraud prevention tools for secure transactions
- User-friendly interface with powerful reporting capabilities
- Dedicated customer success team for personalized support.
Cons of Adyen:
- Customer support response times can be slow for urgent issues
- Limited payment terminal options for in-person transactions
- Platform complexity may be challenging for non-technical users
- Potential for high fees and hidden costs.
4. PayPal

PayPal is a globally recognized payment gateway, making it a trusted choice for businesses of all sizes. Key features of PayPal are:
- Support for multiple payment methods like cards, bank transfers, and PayPal balances
- Operates in over 200 countries with support for multiple currencies and currency conversion
- Strong security measures, including fraud protection and encryption
- PayPal also interacts with the customer’s bank account to verify funds and implement fraud protection measures before completing the transaction.
- Buyer protection feature to encourage trust and enhance customer experience
- Point-of-sale systems for in-person transactions.
Pros and cons of using PayPal payment gateway
Pros of PayPal:
- Easy to set up and use, with a user-friendly interface
- Widely accepted and integrated with most eCommerce platforms, including Magento
- Global reach and multi-currency support simplify international transactions
- Versatile payment options, including bank transfers and PayPal balances
- Security features like fraud and buyer protection boost trust.
Cons of PayPal:
- High transaction fees, especially for international and business payments
- Potential for account holds and restrictions without warning
- Challenges in resolving disputes through customer support
- Limited flexibility for some businesses, with restrictions on multiple activities
- Risk of dependency on a single payment provider.
5. 2Checkout (Verifone)
2Checkout (now Verifone) is a global payment gateway known for its all-in-one platform, combining payment processing with tools like subscription management and tax compliance. Besides, 2Checkout is known for:
- Support for multiple currencies and payment methods, including PayPal and credit cards
- Merchant of Record services for handling tax compliance and local regulations
- Advanced subscription management tools for recurring billing
- Fraud protection to secure transactions and mitigate risks
- Easy integration with Magento and other shopping carts.
Pros and cons of using 2Checkout payment gateway
Pros of 2Checkout:
- Competitive transaction discount rates (TDR) compared to competitors
- Robust APIs for customization and integration
- Reliable platform for subscription management and cart functionality
- Global reach simplifying international sales
- User-friendly interface and easy implementation process.
Cons of 2Checkout:
- Occasional downtimes and technical glitches, though improved over time
- Risk of account suspension due to policy complexities
- Delays in implementing customization requests
- Currency conversion fees for local payouts, adding unexpected costs
- Lack of live chat support, relying on email for assistance.
6. Klarna
Klarna is a Swedish fintech known for its Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) service, letting customers split purchases into interest-free installments while boosting sales for merchants. Klarna is also known for:
- Support for various payment methods in one platform
- Simplified administration by consolidating payment providers
- Wide acceptance across numerous online retailers
- Potential to increase sales and customer loyalty with flexible payment options.
Pros and cons of using Klarna payment gateway
Pros of Klarna:
- Drives higher sales and average order values through BNPL options
- Offers convenience and flexibility for customers managing payments
- Simplifies operations by supporting multiple payment methods in one platform
- Enhances customer loyalty through flexible payment terms
- Widely recognized and accepted across a large number of retailers.
Cons of Klarna:
- Poor customer support for merchants, with slow response times and limited resolution options
- Challenges with merchant approval and inconsistent identity verification processes
- Potential for customer financial strain, with risks of late fees and negative credit impacts
- Reports of technical glitches and a laggy app experience
- Lack of transparency and flexibility in payment terms, such as limited options for early payments or single, one-time payments in advance.
7. Mondu
Mondu is a unique payment gateway focusing exclusively on B2B payments, specializing in BNPL solutions for B2B transactions that offer flexible payment terms to improve cash flow and reduce default risks. Besides this standout feature, Mondu is also known for:
- Seamless integration with online checkouts, telesales, and field sales
- Real-time credit and fraud checks using machine learning
- Merchants receive upfront payment while Mondu assumes default risk
- Administrative support for collections and dunning processes.
Pros and cons of using Mondu payment gateway
Pros of Mondu:
- Tailored for B2B commerce with flexible payment options
- Improves cash flow by paying merchants upfront
- Increases sales and average order values by offering payment flexibility
- Reduces administrative burdens, allowing businesses to focus on operations
- Simple integration with multichannel sales environments.
Cons of Mondu:
- Stringent account approval process may exclude some businesses
- Limited compatibility with certain suppliers, creating potential friction
- Slow customer support response times can delay issue resolution
- Insufficient transparency on payment structure and merchant fees
- Limited insights into broader payment gateway functionalities.
8. Planet
Planet is a financial services provider known for combining payment solutions with VAT refund services and integrated technologies, tailored for industries like retail and hospitality.
Key features:
- Multi-currency payment processing for global commerce
- Credit card processing and integrated financial services
- Cloud software solutions for retail and hospitality sectors
- Presence in 120+ markets, supporting international transactions
- VAT refund services tailored for the tourism industry.
Pros and cons of using Planet payment gateway
Pros of Planet:
- Strong global presence, ideal for businesses with international operations.
- Comprehensive approach, combining payments with software and technology solutions.
- Industry focus, particularly retail and hospitality, with tailored offerings.
- Decades of experience in financial services, enhancing reliability.
- Emphasis on positive customer experiences and digital innovation.
Cons of Planet:
- Limited information on core payment gateway functionality compared to leading competitors.
- Primary focus on VAT refunds, potentially sidelining traditional payment features.
- Unclear details on integration, pricing, and security measures.
- Unverified suitability for small to medium-sized businesses outside its target industries.
9. Bolt

Bolt is a checkout platform known for its “One-Click Checkout,” simplifying payments and reducing cart abandonment for Magento merchants.
Key features:
- One-Click Checkout for faster, frictionless payments
- Fraud Chargeback Guarantee to protect against financial losses
- Bolt Network to connect retailers with millions of shoppers
- Seamless integration with eCommerce platforms like Magento
- Mobile-friendly checkout design for improved user experiences.
Pros and cons of using Bolt payment gateway
Pros of Bolt:
- Optimized checkout experience increases conversion rates
- Strong fraud protection ensures peace of mind for merchants
- Easy integration with Magento and other platforms minimizes technical challenges
- Access to the Bolt Network may expand the customer base
- Excellent customer support, praised for responsiveness and helpfulness.
Cons of Bolt:
- Limited details on payment gateway features like supported methods and fees
- Potentially higher fees compared to other gateways, which may deter cost-sensitive businesses
- Occasional bugs and issues with the platform could disrupt checkout
- Security concerns when used on shared devices, posing risks in certain retail settings.
How to integrate a payment gateway in Magento 2

Installing a payment gateway in Magento 2 is not a complicated process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through it.
- Once you’ve chosen a payment gateway that fits you the best, you’ll need to sign up for a merchant account with your payment gateway provider. Your merchant account will give you the login credentials you need to connect the payment gateway to your Magento store.
- From the Magento Marketplace or your payment gateway provider’s website, download the payment gateway extension. Follow the instructions to install it.
- Once the extension is installed, you’ll need to configure the settings in your Magento store. Enter your merchant account info, select your payment methods, and customize any additional features, such as recurring billing and subscriptions.
- Finally, test your payment gateway by making a test transaction. This will ensure payments are processing correctly and updating your Magento orders.
Integrating a payment gateway is straightforward, but if you want to ensure everything is set up correctly and tailored to your Magento store, a professional Magento developer can handle it seamlessly for you. Partnering with an expert guarantees a smooth integration process and optimized functionality.
Conclusion: Choosing the right payment gateway for your Magento store
Your payment gateway isn’t just a back-end tool—it’s the final step in your customers’ shopping journey. A poor choice can lead to abandoned carts, lost sales, and frustrated customers.
Every hiccup at checkout risks breaking customer trust. In today’s competitive market, a smooth and secure checkout isn’t optional—it’s essential. Businesses that prioritize the right payment gateway see fewer abandoned carts, happier customers, and sustainable growth.
Your customers deserve a seamless checkout. Choose a payment gateway that aligns with your goals and ensures your Magento store thrives!

Frequently Asked Questions
Which of the Magento payment gateways are the best?
The right payment gateway for Magento depends on your business needs. Some of the most popular options include PayPal, Stripe, 2Checkout, Klarna, and Adyen. Each of these gateways offers robust security, multi-currency support, and seamless Magento 2 integration, but their specific features and transaction fees will determine whether it is the best fit for you.
What is a Magento payment gateway?
A Magento payment gateway is a secure way for online transactions to communicate between your eCommerce store and payment processors. It allows you to accept credit cards, digital wallets, and other payment methods while meeting the highest security standards.
How do I set payment methods in Magento?
Access the Magento 2 Admin Panel and navigate to Stores > Configuration > Sales > Payment Methods. Here, you can enable or disable payment methods, configure their settings, and save your changes to update your store. Then, select your desired gateway, configure its settings, and enable it for your store.
How much does Magento payment gateway cost?
The cost of a Magento payment gateway varies by provider. Most gateways charge a transaction fee, which typically falls between 2.6% and 4% of the total sale amount. Some gateways also charge a flat fee per transaction, such as $0.30. Additionally, some providers may charge monthly fees or setup costs. Be sure to explore each gateway’s pricing structure to get an accurate picture of the total costs involved.
What are Magento 2 payment restrictions?
Magento 2 payment restrictions allow you to control which payment methods are available to customers based on a range of conditions. These conditions might include shipping methods, customer groups, product attributes, order totals, or geographic locations. By applying payment restrictions, you can tailor the payment options available at checkout to fit your business policies and customer expectations.
Explore our popular Adobe Magento services
Ready to upgrade your Magento store’s checkout experience? Reach out to us, and we’ll help you choose the best payment gateway and install it in your Magento store!
About scandiweb
scandiweb is a leading eCommerce agency, specializing in Magento development, payment gateway integrations, and end-to-end digital services. With a proven track record of delivering tailored solutions for global brands, scandiweb combines technical expertise with a client-first approach to help more than 600 businesses thrive online.
The post Top 9 Best Magento Payment Gateways for Your Online Store in 2026 appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Add-to-Cart Best Practices in 2026: Nudging Prospects to Buy appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The add-to-cart moment is no longer just a functional step in the buying journey — it’s a critical decision point where intent can either be reinforced or lost.
In 2026, users move fast, shop across devices, and expect immediate, clear feedback when they take action. Adding a product to the cart should feel unmistakable, reassuring, and momentum-building. When that moment is unclear, delayed, or easy to miss, even high-intent shoppers can lose confidence, get distracted, or abandon the purchase altogether.
That’s why add-to-cart UX has evolved from simple confirmation patterns into a powerful conversion lever. When done right, it reassures users, reduces friction, and subtly nudges them toward checkout — without feeling pushy.
Below, we’ll break down modern add-to-cart best practices that help turn buying intent into completed purchases in 2026.
1. Emphasize the cart icon
It isn’t enough to just add a small number to the cart icon to indicate how many products have been added to the cart. Once products are added, the cart icon should also change in color—making it more prominent—so it catches the user’s attention more.

2. Show a mini cart or a cart pop-up
In addition to an emphasized cart icon, there should be a prominent event on the page when the user adds a product to the cart. And the add-to-cart moment can be highlighted by displaying a mini cart or a cart pop-up.
A mini cart can appear in different ways, but here are two examples:
- As a notification box originating from the cart icon. The box usually shows which product was added to the cart (photo + title), item quantity, order subtotal, and CTAs to Checkout or View Cart
- As a slide-out mini cart. As users add products to the cart, an animated cart slides out, usually from the right side of the screen. It shows the same information as above but works especially well as the animated movement on the page is very prominent. Even better, the rest of the screen is grayed out until the mini cart is closed—so the add-to-cart event cannot be missed.
An alternative to the mini cart is the cart pop-up. Instead of sliding out from either the cart icon or one side of the screen, the cart pops up in the middle of the screen. Of course, it shows the main cart information and the CTAs, too. And it’s hard to imagine how a user can miss it when they have to close the pop-up first before they can continue shopping or take any other step.
This might be considered as an additional step between adding a product to the cart and the checkout; then again, it guarantees that the user doesn’t miss whatever is added to their cart.
3. Upsell and cross-sell
The primary goal of the mini cart is to communicate to the user what is added to their cart and the cart subtotal. Nevertheless, the mini cart is also a great opportunity to use upsell and cross-sell techniques and nudge the user to spend more.
The trick is to make this additional shopping experience as smooth as possible—users should be able to add more items to the cart with just one click.
4. Communicate benefits
To encourage users to finish the purchase, it works to communicate to them the additional benefits they are getting. For example:
- If the user qualifies for free shipping, let them know.
- If users will get free samples or other gifts when they meet certain conditions, they should be clearly informed about it so they can have more motivation to move along the user journey.
- If the products have great reviews or extended guarantees, they can be communicated as reassurance for users that they won’t regret their purchase.
- If the company accepts returns, emphasizing it will help users who still have doubts about a purchase feel more comfortable proceeding with the order.
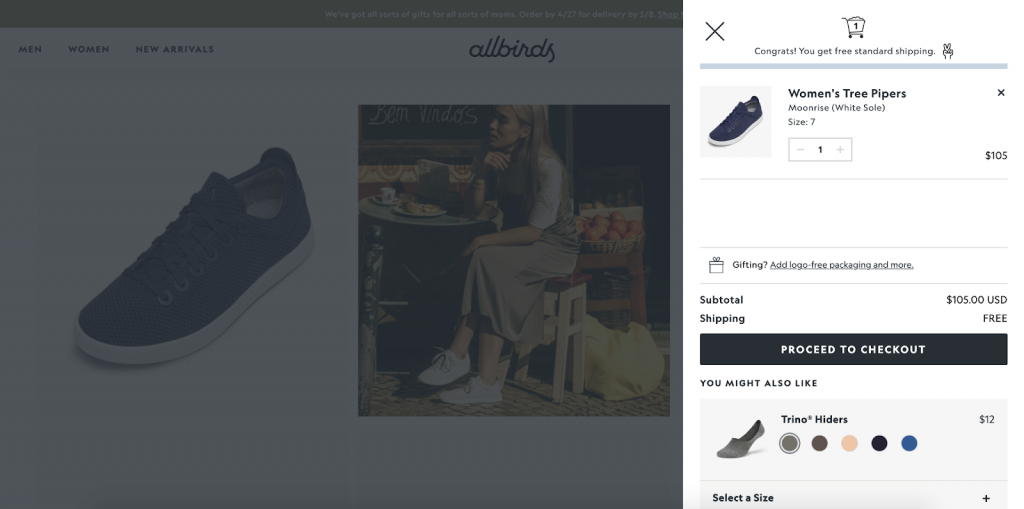
5. Add express checkout options
If express checkout options are available, they should be communicated right in the mini cart or cart pop-up. It makes it more convenient for users to complete the checkout, thus providing a better shopping experience for them. Instead of going through the checkout page, they can proceed to complete their purchase right from whichever page they are currently.
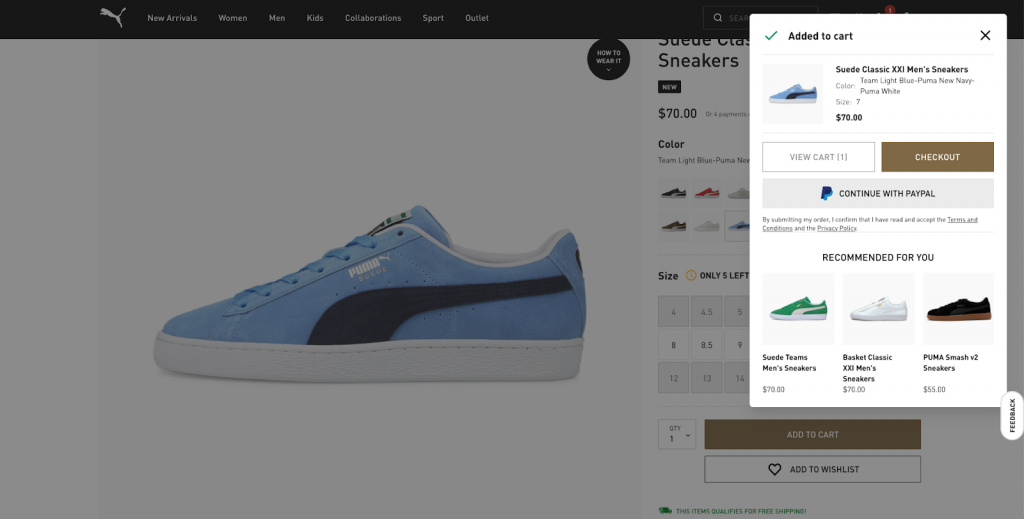
6. Reinforce intent with smart, contextual feedback
In 2026, static confirmations are no longer enough. Users respond better to contextual, real-time feedback that reflects their situation.
This can include:
- Messaging that adapts based on cart value (e.g. progress toward free shipping)
- Dynamic reassurance such as delivery estimates or stock availability
- Personalized recommendations based on browsing or cart history
The goal isn’t more information, it’s relevant information that reinforces the decision the user just made.
6. Optimize add-to-cart for mobile-first behavior
Most add-to-cart interactions now happen on mobile, where attention spans are shorter and screen space is limited.
Effective mobile add-to-cart UX should:
- Keep feedback within the thumb zone
- Use sticky or persistent add-to-cart elements on long product pages
- Avoid full-screen interruptions unless they clearly add value
If users have to hunt for confirmation or struggle to reach the next step, friction creeps in fast.
7. Reduce friction with persistent and cross-device carts
Shoppers rarely complete purchases in one session or on one device. Losing cart state means losing momentum.
Best-in-class add-to-cart experiences in 2026:
- Persist carts across sessions and devices
- Restore cart contents instantly when users return
- Clearly communicate that items have been saved
This continuity reassures users and removes the mental load of “starting over.”
Wrapping Up
In 2026, great add-to-cart UX is about more than visibility — it’s about reinforcing intent at exactly the right moment.
From clear visual feedback and mini carts to smart personalization, mobile-first design, and frictionless checkout paths, every add-to-cart interaction should move the user forward with confidence. Small improvements at this stage can have an outsized impact on conversion rates and average order value.
When the add-to-cart experience is clear, fast, and reassuring, users don’t just add items — they finish what they started. And that’s where consistent, scalable growth really begins.
If you need help implementing these improvements in your eCommerce store, get in touch with Scandiweb’s Growth Team today. Book a free consultation to learn about our conversion optimization program and how we can help you achieve your conversion goals.
The post Add-to-Cart Best Practices in 2026: Nudging Prospects to Buy appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Driving 15% AOV Increase with Personalization and Marketing Automation appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>We decided to give scandiweb full ownership of our eCommerce ecosystem. It was the right choice!
Oskar Röös
CIO at Byggmax
About
Byggmax is a leading DIY retailer in the Nordic region, operating 160+ physical stores across three countries alongside a large-scale eCommerce operation, offering a catalog of more than 55,000 construction, renovation, and home improvement products.
In 2023, their clients were affected by inflation and growing energy prices. This meant Byggmax had to find ways to increase order value without adding friction to the buying experience or increasing acquisition spend. To reach ambitious revenue targets, they integrated a new personalization and marketing automation suite to increase average order value (AOV) and conversion rates across all markets.
Problem
Existing eCommerce demand was not translating into sufficient value per order.
Byggmax operates in a price-sensitive category with tight margins and high transaction volume. External pressures from inflation and rising operational costs heightened the importance of extracting greater value from existing demand. Small inefficiencies in order value compound quickly when applied across thousands of orders.
Email marketing was already in use, but its impact on cart size and purchases was limited.
The issues showed up as:
- Average order value limiting revenue efficiency
- Email activity focused on communication, not fully utilized to influence purchasing behavior
- Limited use of personalization
- Missed opportunities to surface relevant products from a large catalog
- Difficulty scaling manual optimization for high transaction volumes.
Solution
Marketing automation foundation
We integrated Dotdigital and introduced a new marketing automation setup to support core customer journeys and establish a consistent automation backbone for email communication:
- Automated abandoned cart emails
- A structured welcome flow
- Inactive customer re-engagement emails.
Personalization embedded into automation
To more precisely influence purchasing behavior, we implemented Dynamic Yield AI-powered personalization to enable 1:1 personalization at every step of the user journey. Personalization extended into email content, where product recommendations were dynamically generated based on customer behavior.
Content and recommendations were tailored for 10 distinct customer segments, allowing Byggmax to surface relevant products from its 55k+ catalog without manual curation.
Email and SMS working together
Alongside email, SMS was introduced to support high-impact moments, such as post-purchase updates and one-time promotional campaigns. SMS complements email automation by providing timely, transactional, and promotional touchpoints where immediacy matters.
Testing tied to commercial impact
We ran a structured A/B testing program for the website and email content. Variants were evaluated based on measurable commercial performance: increase in average order value and direct revenue impact.
All personalization, automation, and data usage were implemented in compliance with the Swedish Data Protection Act, ensuring that customer data handling met regulatory requirements while scaling across markets.
Outcome
Personalization and marketing automation have become core to how Byggmax supports large-scale eCommerce growth:
- Personalization and marketing automation supports eCommerce growth on a path to $1B/year
- Average order value increased by 15%
The combination of automated email flows, 1:1 personalization for 10 customer segments, and coordinated email and SMS communication allowed Byggmax to extract more value from existing demand while maintaining operational control and regulatory compliance.
If revenue growth is constrained by order value or conversion efficiency, we can help you identify where personalization and automation will have the highest impact.
The post Driving 15% AOV Increase with Personalization and Marketing Automation appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Restructuring Email For Customer Intent Drives 24% Revenue Growth appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>CircuitMess is a global eCommerce brand creating educational DIY electronics kits that teach children and adults how technology works through hands-on learning. The business sells directly to consumers online, serving a highly engaged but diverse audience spanning different age groups.
With products that often require explanation, education, and follow-up engagement, customer journeys play a critical role in conversion and repeat purchases. Email was already part of CircuitMess’s marketing mix, but its impact on revenue was limited.
Problem
Email activity was not aligned with customer journeys, limiting its impact on revenue growth.
CircuitMess had email campaigns and basic automations in place, but the channel was not built around customer journeys or buying behavior. As a result, email was underperforming relative to its potential and was not contributing meaningfully to overall revenue growth.
The issues showed up as:
- Emails not aligned to where customers were in their journey
- Limited use of lifecycle logic to guide customers toward purchase
- Generic messaging that didn’t reflect product complexity or intent
- Missed opportunities to educate, nurture, and re-engage users.
Solution
We rebuilt CircuitMess’s email program around clear lifecycle stages and customer intent. Each journey had a defined role in guiding customers with valuable, clear messaging rather than simply promoting offers. We kept our focus on practical improvements that could directly impact revenue, leveraging the channel’s existing elements and strengthening them where measurable impact was achieved.
Rebuilding core automated sequences
Core automated email sequences were rebuilt to improve structure, clarity, and conversion impact, without introducing new complexity:
- Updated layouts designed to improve readability and engagement
- Refined copy to reduce friction and support conversion
- Stronger conversion triggers within existing automations
- Ensuring automated emails followed a consistent structure and hierarchy.
Conversion-driven email templates
We created a new, unified template system for campaigns and automations, improving visual hierarchy to guide attention toward primary actions and reducing unnecessary elements that distracted from conversion. Templates were treated as conversion assets, allowing us to compare and test results reliably.
Opt-in growth and audience capture
To strengthen the email channel’s input quality, new opt-in forms were implemented, allowing email performance improvements to scale with list growth:
- Improved placement and design of sign-up forms
- Focus on capturing higher-intent subscribers
- Alignment between opt-in messaging and downstream email content.
Continuous testing and optimization
We introduced an ongoing testing approach to improve performance over time by applying A/B testing to email designs, content, and CTAs to understand what drove stronger engagement and revenue contribution. Higher-performing variants were identified and continued, while underperforming elements were refined or removed. Testing was applied consistently across campaigns and automated emails.
Audience segmentation
We refined segmentation and targeting to ensure each template performed effectively across audience groups, with adjustments made to targeting based on engagement behavior. Email content got aligned with product launches and seasonal events to support sales and retention.
Outcome
scandiweb’s team created 51 new email templates for campaigns and automations, resulting in a 24% increase in eCommerce revenue driven by new emails.
The redesigned templates created a consistent, conversion-focused foundation. Instead of isolated improvements, performance gains now compound as new campaigns and automations reuse the same proven structures.
If your email program is live but not driving measurable growth, we can help you rebuild it around customer journeys that convert.
The post Restructuring Email For Customer Intent Drives 24% Revenue Growth appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Building a €150K/Month Lifecycle Revenue Engine in 5 Markets appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>FELCO is a Swiss premium brand recognized globally for its professional pruning tools and garden equipment in multiple international markets, serving professional and enthusiast customers through direct-to-consumer eCommerce.
With a broad product catalog and customers returning over long usage cycles, FELCO’s eCommerce growth depends on repeat purchases, timing, and relevance across markets. As the business expanded internationally, lifecycle marketing became a critical lever for consistently and at scale monetizing existing demand.
Problem
FELCO lacked a unified lifecycle marketing engine capable of driving revenue consistently market-by-market.
Email activity existed, but it was not structured as a scalable revenue system. They had incomplete lifecycle automations with varied market-specific execution and uncoordinated personalization for regions and languages.
The issues showed up as:
- Fragmented lifecycle revenue potential
- Different engagement and personalization by region
- Email not operating as one of the business’s primary revenue channels.
Solution
We built a centralized email and SMS lifecycle revenue engine, designed to operate consistently across markets while remaining locally relevant.
Lifecycle automation
All core lifecycle automations were designed, built, localized, and launched to form the backbone of lifecycle revenue generation:
- Opt-in and list growth mechanisms
- Welcome flows
- Browse, cart, and checkout abandonment sequences
- Post-purchase journeys
Multi-market and multi-language rollout
The entire lifecycle system was launched within 30 days – localized across 5 markets and delivered in 3 languages. We adapted email designs to maintain brand consistency while supporting local content and language requirements.
SMS channel implementation
Alongside email, we implemented an SMS channel focused on high-intent touchpoints and key seasonal moments, ensuring messaging complemented, rather than duplicated, email journeys.
Ongoing optimization
Performance data was actively used to refine content and offers, optimize timing and cadence, and improve engagement and cross-market revenue contribution. Segmentation frameworks reflect different buyer profiles and regional behaviors, enabling more relevant communication at scale.
Outcome
Lifecycle marketing shifted from fragmented execution to a central, scalable revenue system, capable of supporting international growth without increasing operational complexity.
- €150K in monthly revenue established from lifecycle marketing
- Email and SMS became one of FELCO’s biggest marketing channels
- All core lifecycle automations were live across 5 markets and 3 languages within 30 days.
If your eCommerce business operates in multiple markets but lifecycle revenue remains fragmented, we can help you build a centralized email and SMS engine that scales globally without losing local relevance. Let’s talk!
The post Building a €150K/Month Lifecycle Revenue Engine in 5 Markets appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>The post Launching Email from Zero with 1176% ROI During BFCM appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>MyNextMattress is a leader in the UK mattress industry. The business operates in a category where purchase decisions are infrequent, high in consideration, and heavily influenced by timing and promotions.
Email had never been used as a sales channel for MyNextMattress. This made the approaching Black Friday and Cyber Monday a practical test case — a short, high-intent window where the company could quickly determine whether email was worth investing in as a revenue channel at all.
Problem
Going into BFCM without any email channel in place, MyNextMattress couldn’t re-engage high-intent visitors or generate revenue during peak demand.
There was no email infrastructure in place, no lifecycle flows, no subscriber base, no campaign history, and no baseline for email performance, since email had never been tested or proven as a revenue channel for the business.
The issues showed up as:
- Peak traffic would come and go, with no way to reconnect with visitors
- Purchase consideration is lost after the session
- Email remains an untested channel with no evidence to support future investment.
Solution
To validate email as a revenue channel within a limited timeframe, we focused on rapid execution with the goal of proving email’s revenue potential during BFCM.
Email channel launch
We established an end-to-end email marketing strategy, including planning, design, copy, technical setup, and readiness for peak traffic.
High-intent BFCM campaigns
We designed and built three high-impact BFCM email campaigns, fully aligned with on-site promotions. Each campaign was created to support urgency and drive conversions. In a focused scope, we:
- Concentrated on the highest-intent moments
- Aligned offers and messaging with the eCommerce experience
- Prioritized speed and clarity over long-term complexity.
Performance-driven insights
Data from campaign performance were used to assess revenue contribution, validate email as a viable growth channel, and define next steps for scaling email and automation beyond BFCM.
Outcome
- £10,000+ in incremental revenue generated from email marketing during BFCM
- 1176% ROI
- Every £1 invested returned ~£12.75 in revenue
MyNextMattress email moved from non-existent to revenue-generating within a single peak sales window.
If email isn’t part of your eCommerce growth model yet, or isn’t performing like you want it to, we can help you launch it with a clear revenue goal.
The post Launching Email from Zero with 1176% ROI During BFCM appeared first on scandiweb.
]]>