Shopify provides a stable foundation for brands seeking a more manageable and reliable tech stack, as well as a storefront that’s easy to maintain over time. Many teams also use the migration as an opportunity to update outdated data and close gaps created by years of patches and workarounds.
The move to Shopify works best with a structured approach and a realistic understanding of what needs to be rebuilt, imported, or reconfigured.
This guide breaks down the Shopify migration process into clear phases, starting with an assessment of your current setup, all the way to a live, tested Shopify store. If you’re preparing for a move to Shopify, this walkthrough will help you plan ahead and build a setup that supports steady growth from day one.
Common challenges before and after migration
Most teams move to Shopify expecting things to get easier, with fewer bugs, fewer delays, and more flexibility. And in many cases, that’s exactly what happens. But for brands with complex operations or legacy systems, the transition can expose deeper issues and sometimes create new ones if not managed carefully.
These are some of the most common challenges we’ve seen before and after replatforming:
Disconnected systems
Data doesn’t flow cleanly between tools. ERPs, CRMs, PIMs, and OMSs all need to be connected with care. Without the right architecture, syncing issues and data silos continue even after the migration.
Duplicated stores for international markets
Shopify is often set up as one store per market, which leads to duplicated catalogs and separate promotions that require more manual work across regions. Without a proper plan, complexity increases rather than decreases.
Heavy reliance on apps
Quick fixes often come in the form of third-party apps. Over time, this can create potential issues when one app fails or conflicts with another, compromising the entire flow.
Checkout limitations
Shopify offers limited flexibility for custom flows – checkout adjustments tied to region, pricing logic, or customer type can be challenging to implement natively.
SEO drops
If redirects, metadata, structure, and other tech SEO essentials aren’t handled properly, a migration to Shopify can lead to traffic losses. And recovery takes time, especially if the site had strong organic performance before migration.
No single source of truth
Even after migrating, many brands still struggle with fragmented data. Customer records don’t update in real-time, and analytics fail to reflect the complete picture. Without proper integration planning, the migration only moves the problem to a new platform.
Next, let’s walk through the Shopify migration process step by step.
Step 1: Audit your current platform
Before planning a move to Shopify, take a close look at your existing setup. A technical audit should go beyond surface-level issues. Many platforms evolve through quick fixes and ongoing adjustments, resulting in unpredictable behavior and a setup that’s difficult to manage. Reviewing how your store currently functions can reveal which parts of the system need to be replaced and which ones still serve their purpose.
Start by mapping out:
- Where your data lives (product, inventory, customer, order)
- Which tools are connected and how well they sync
- How promotions, checkout flows, or product bundles are currently handled
- Any third-party apps that feel essential but are adding complexity or cost
Next, look at content and UX:
- Are product pages consistent and easy to update?
- Does the mobile experience reflect your brand?
- Is it clear where the technical limitations are slowing down marketing or merchandising?
At this stage, it’s useful to ask: if your current store were wiped tomorrow, what would you rebuild the same way? And what would you change?
Step 2: Plan your Shopify setup
Once you understand how your current store operates, the next step is creating the foundation of your new Shopify environment. Decisions made here influence your data structure, daily workflows, performance, and the level of flexibility you’ll have long term.
Begin with the Shopify plan that best suits your needs. Stores with extensive catalogs, complex rules, or multiple markets often benefit from Shopify Plus due to its expanded limits and access to advanced features. Smaller setups can run smoothly on standard Shopify. The goal is to choose a plan that supports future growth without requiring major restructuring later.
Next, define the technical layout of your store. Some operate from a single Shopify store and manage regions through Shopify Markets. Others maintain separate stores for different countries or business units. It depends on pricing rules, tax logic, language requirements, fulfillment locations, and operational ownership inside the company.
This stage is also the time to outline integrations. ERPs, PIMs, OMSs, CRM platforms, and marketing tools all need clear data paths. If your current stack contains fragile connectors or outdated plugins, note these as items to rebuild or redesign during the migration. A dependable integration plan helps avoid issues that often appear after launch, like delayed stock updates, inconsistent product data, or incomplete customer profiles.
In parallel, prepare how teams will work inside Shopify. Roles, permissions, collaborator access, and staging environments should be arranged early, creating a controlled setup and a stable base.
Step 3: Clean and export your data
Migration also exposes the quality of the data you’ve been working with and how much of it needs improvement.
Start with your product catalog. Check for duplicate SKUs, inconsistent naming, outdated items, or mismatched attributes. If different teams have been adding products over time, structure and formatting may vary across collections. Fixing this now will prevent downstream errors during import and create a better shopping experience once live.
Review your customer database next. Identify test records, unsubscribed contacts, and incomplete profiles. Decide which segments are still active and worth migrating. Cleaning customer data before export also improves targeting accuracy for marketing flows once Shopify is live.
For orders, confirm which records are needed for historical reporting. Some brands choose to migrate all order history, while others only keep recent data. Shopify allows historical orders to be imported for reference, but they won’t behave like native orders – so plan how you want to access and report on past activity.
Most platforms support CSV exports. If your setup is more custom, API access or direct database extraction may be required. Either way, the export phase is an opportunity to restructure and clarify how data will be stored within Shopify.
scandiweb’s team often runs custom cleanup workflows at this stage. For example, during one migration, thousands of SKUs needed to be standardized before import, not just for accuracy, but to ensure compatibility with advanced search and filtering logic later on. Well-prepared data helps the rest of the migration proceed more efficiently. It also reduces support tickets after launch, since product visibility, pricing, and customer records are already in order.
Step 4: Import data into Shopify
Once your product, customer, and order data have been reviewed and cleaned, you can begin importing it into Shopify. This step often happens in phases, starting with a controlled test, followed by a broader import once everything checks out.
Product imports
Shopify supports CSV uploads for standard product fields such as titles, descriptions, pricing, inventory, and variants. For more complex catalogs, additional data like metafields, vendor references, or grouped items may need to be imported using Shopify’s Admin API or other tools. Some projects also rely on custom scripts for better control.
After the initial upload, check the results for errors. Missing images, broken variant logic, or inconsistent pricing structures are common issues. Bulk editing tools in Shopify can help resolve minor issues quickly, but more significant discrepancies may require rework at the source.
Collections and categories
In Shopify, collections can be either manual (where the team selects products) or automated (where products are included based on tags, price, or other conditions). Decide early which model fits best. Automated collections save time for larger catalogs but require consistent product data. Manual collections give more flexibility for merchandising, campaigns, or curated selections.
If your previous platform used custom category logic or allowed deep nesting, prepare for some adjustments. Shopify structures categories differently, and large taxonomies often need simplification. It’s also important to plan how URLs for collections will be handled, especially for SEO continuity.
Customer and order imports
Customer data can be imported via CSV, but certain details will not be carried over, including passwords and saved payment methods. Expect to send account activation emails once the store is live. This part of the migration should be timed carefully to avoid confusion or support overload.
Historical orders can also be imported for reporting purposes. They won’t behave like new Shopify orders (e.g., no refunds or fulfillment actions), but they help preserve account context and lifetime value tracking.
The goal here is stability, ensuring that the data appears in the right place and functions reliably for customers and your team.
Step 5: Configure payments, shipping, and tax
Once your store structure and data are in place, it’s time to set up the core functions that power transactions and fulfillment. Payment gateways, shipping rules, and tax settings each carry operational weight, and gaps in this step often show up as customer complaints or failed orders that translate into lost revenue.

Payment methods
Start by enabling your preferred payment providers. If you’re eligible for Shopify Payments, it’s typically the most common option. It covers major credit cards and wallets like Apple Pay or Google Pay, and gives access to features like fraud protection, chargeback handling, and consolidated reporting.
If your store sells internationally, activate local methods commonly used in your target regions. Payment preferences vary widely by market, and improving checkout familiarity often improves conversion rates. Shopify supports location-based logic to display relevant payment methods to each shopper.
Any previously saved payment methods from your old platform will not carry over, due to compliance rules. Customers will need to re-enter their details on their next purchase, so plan communications around this to prevent confusion.
Shipping setup
Shipping rules in Shopify are managed through zones and profiles. Define where you ship and which methods apply to each region:
- Flat rates
- Real-time carrier rates
- Local delivery
- Free shipping thresholds.
If you use a 3PL, warehouse network, or dropshipping setup, connect those providers early. Make sure they’re fully integrated before launch to avoid fulfillment delays. Shipping apps or native Shopify integrations can support this, depending on your logistics setup. Test different scenarios – local orders, international deliveries, split shipments – to confirm that shipping charges and workflows are accurate.
Taxes and compliance
Shopify can calculate taxes automatically based on store location and customer address. In more complex regions, or when selling across borders, additional configuration may be needed.
Enable Shopify Markets if you plan to support multiple currencies, duties, or tax-inclusive pricing. You can also integrate third-party tools for more granular control, especially in jurisdictions with changing tax laws. Remember – Misconfigured tax settings can trigger penalties or create liabilities post-launch.
Quick test checklist
Before moving forward, confirm that:
✓ All required payment methods are active and display correctly by region
✓ You’ve tested real transactions with at least two payment types (e.g., credit card + local method)
✓ Shipping rates calculate correctly for key zones
✓ Fulfillment logic works across split shipments or multi-warehouse setups
✓ Taxes are calculated correctly based on customer location and product type
✓ Checkout totals reflect the correct currency, tax, and shipping format
✓ Manual and automated order confirmations include all expected details.
Step 6: Protect SEO during migration
Organic traffic is one of the most valuable assets your store has, and also one of the easiest to lose during a migration. Platform changes often shift how pages are structured, how content is displayed, and how URLs are generated. Without a clear SEO strategy, visibility can drop, and recovery can take months.
- Audit your current site to identify which pages bring in the most traffic, generate conversions, or support important keywords. These high-value URLs should be preserved or mapped as closely as possible in your Shopify structure.
Shopify uses a fixed URL format, so some changes will be unavoidable. For example, product pages will always follow the /products/ path. That doesn’t mean performance has to drop, but it does mean you’ll need a detailed redirect plan.
- Create a complete list of old URLs and their new equivalents. Use 301 redirects to guide users and search engines to the right content. Shopify’s built-in redirect manager works for this, and bulk uploads are supported via CSV.
- Migrations also affect metadata, structured data, and internal linking. If your original store used custom logic for canonical tags, breadcrumbs, or product schema, plan how these will be handled in Shopify. You may need theme updates or app support to recreate the same structure.
- Before going live, submit your new XML sitemap to Google Search Console. Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to crawl your Shopify site, catch errors, and confirm that key content is indexed and discoverable. Monitor performance closely for the first few weeks after launch, especially impressions and keyword positions for your most important pages.
Step 7: Design your Shopify store
A redesign during migration offers the chance to improve how products are found, how trust is built, and how easily customers complete a purchase within a framework that supports long-term performance and day-to-day usability.
Shopify themes offer flexible sections, speed improvements, and greater control without heavy developer input. Some brands adapt a premium theme to meet their goals, but you can work with partners to build something entirely custom. If you’re looking for performance and scalability without starting from scratch, options like our Satoshi theme for Shopify can provide a fast, UX-driven foundation that’s easy to adapt and extend.
For stores migrating from legacy platforms, there’s often technical debt embedded in the frontend, manifesting as inconsistent layouts, overlapping styles, and custom scripts that are difficult to update. This is a good moment to reset. Focus on clarity and plan design systems that scale with your catalog and feel consistent from homepage to checkout.
Banners, content blocks, promotional areas, and landing pages should be editable without developer support. If you’re using Shopify Plus, additional options like Shopify Scripts or custom checkout styling may be introduced at this stage.
Where possible, carry forward high-performing layouts from the previous store, especially on product and collection pages. Shopify allows enough flexibility to preserve familiar structures while still upgrading the experience, which helps maintain conversion performance and keeps the transition smooth for returning customers.
Page speed, mobile UX, and navigation logic all contribute to how the site performs post-launch. Keep images lightweight, test on real devices, and avoid unnecessary app installations or features that slow down the experience.
Step 8: Integrate third-party tools & systems
A migration is rarely about the storefront alone. eCommerce operations rely on a network of systems, including ERPs, PIMs, CRMs, marketing tools, analytics platforms, and fulfillment partners.
To account for these integrations, list out every system currently connected to your platform, including internal tools and third-party apps. For each, define what the integration needs to do: push product data, pull order updates, sync customer records, or support segmentation and automation.
From there, map how these systems will interact with Shopify. While some connections can be rebuilt using Shopify’s native APIs or public apps, others may need middleware or custom connectors, especially if your current setup involves multiple sources of truth or large product catalogs.
Common integration points include:
- ERP
- PIM
- CRM/ESP
- OMS/WMS
- CDP/analytics.
Think beyond day one. Integrations often break because they’re built without version control or clear documentation. And definitely consider app usage. Some migrations copy over every tool from the old platform without re-evaluating their value. Use this moment to reduce reliance on apps that introduce overhead or performance issues. Shopify’s ecosystem offers thousands of tools, but not all are worth keeping.
Step 9: Test before launch
This phase is about ensuring the entire system functions properly under real-world conditions.
Start with a soft launch environment. Shopify allows you to preview the store under password protection while running tests in a near-live setting. This gives your team space to validate functionality without exposing the site to customers before it’s ready.
Test core user flows:
- Browsing products and filtering by attributes
- Adding items to the cart
- Proceeding to checkout
- Using discounts
- Using gift cards
- Creating and managing customer accounts
- Completing an order with different payment methods.
Then, test operational flows:
- Order receipt and confirmation emails
- Admin order tracking and status updates
- Fulfillment syncing with warehouses
- Product updates from your ERP or PIM
- Marketing integrations – email triggers, CRM sync, analytics tracking.
Browser and device testing should also be done at this stage. Confirm that the experience is consistent across mobile, tablet, and desktop devices, with a focus on core actions such as search and checkout. Shopify themes are responsive by default, but customizations or third-party apps can introduce display issues in specific environments.
If you’re running multiple stores or markets, test behavior across regions. Pricing, currency, tax display, language, and payment options should all reflect the correct logic for each user location. Shopify Markets can handle this well, provided they are configured and verified correctly.
Real orders should be placed internally to validate the full purchase-to-fulfillment cycle. Test edge cases too, such as partial refunds, canceled orders, or out-of-stock items.
Once the basics are confirmed, focus on monitoring. Use tools like Google Tag Manager, Meta Pixel, or GA4 to track how behavior is recorded across the site. Migrations can disrupt analytics setups, especially if tag placement or page templates have changed. A well-tested store can significantly reduce launch-day stress. It also reduces the number of early support tickets from customers encountering avoidable issues.
Step 10: Launch and monitor your Shopify store
Congrats if you’ve made it to this step in your migration timeline – it’s time to go live! But what happens after launch matters just as much as what leads up to it.
Essentials to go through:
- Remove storefront password protection
- Point your domain to the new Shopify store
- Check that all redirects are active and resolving correctly
- Submit your updated XML sitemap in Google Search Console
- Monitor traffic, behavior, and error reports from the first visit onward.
Once live, confirm that key journeys still perform as expected. Add-to-cart, checkout, payment, integrations, and customer account flows should be tested again in the live environment.
After launch, monitor:
- Page speed and uptime
- Cart and checkout abandonment
- Product visibility and search functionality
- Channel-specific tracking (Meta, Google Ads, TikTok, Klaviyo, etc.)
- Sales trends across devices, countries, and segments.
The goal of every Shopify migration launch is the same: a stable, accurate, and responsive store that customers can trust.
Case study: Magento 1 to Shopify migration for J.R. Dunn
J.R. Dunn, a leading U.S. luxury jeweler and authorized Rolex retailer, partnered with scandiweb to move from Magento 1 to Shopify, modernizing their digital store while preserving the depth and elegance of their brand experience.
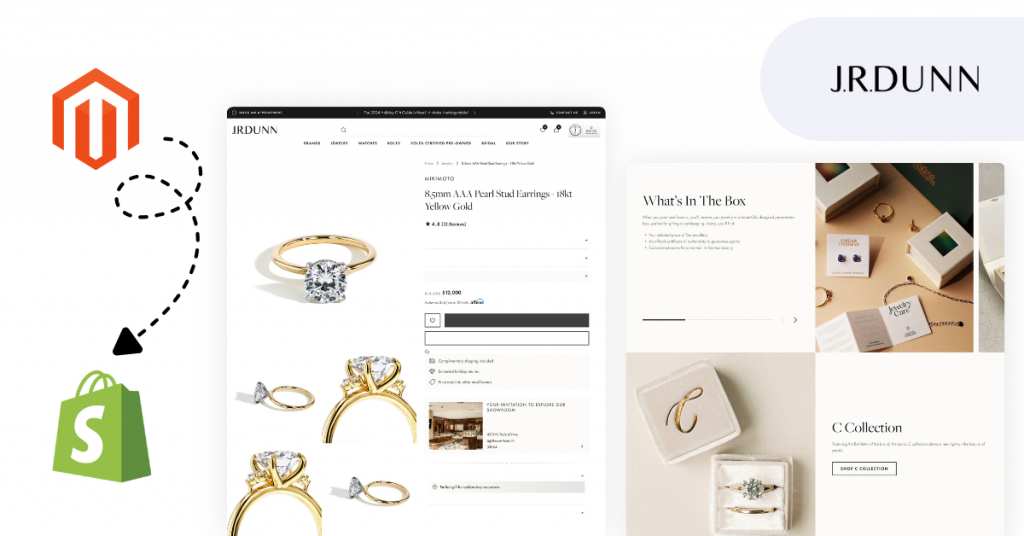
The project involved migrating a highly customized catalog of over 150,000 diamonds, with complex filtering, multi-vendor feeds, and legacy data structures. Out-of-the-box tools couldn’t provide the level of control required, so we built a custom diamond management app to import product data from five vendors, handle live pricing and availability, and integrate directly with Shopify Admin for product management and reservations.
To support advanced product discovery, we also integrated Fast Simon for smart faceted filtering and instant recommendations across a high-SKU catalog. We developed custom storefront features, including a native Ring Builder tool, without third-party dependencies to ensure long-term performance and stability. For design, we used the Satoshi theme, tailored for a luxury presentation.
Results
- 150,000+ diamonds imported via custom app
- 72,000 historical orders and 68,000 customers migrated
- 1,000+ categories and 25,000+ products restructured
- Full SEO migration with a 100 SEO score at launch
- Future-ready architecture for ERP and automation extensions.
Read the full J.R. Dunn Shopify migration case study here.
Shopify migration checklist
Let’s put it all together – use this checklist to track progress across the full migration process!
Platform audit
✓ Identify pain points, limitations, and legacy issues
✓ Map all integrations and third-party tools
✓ Review catalog structure, content quality, and data accuracy
✓ Evaluate technical performance, site speed, and UX consistency
Shopify setup
✓ Select the Shopify plan
✓ Configure account settings, staging access, and roles
✓ Plan architecture: single vs multi-store, Shopify Markets
✓ Outline integration paths for ERP, PIM, OMS, CRM, and ESP
Data cleaning & export
✓ Clean product data, SKUs, images, and variants
✓ De-duplicate and segment customer records
✓ Export historical orders if required
✓ Prepare clean CSVs or API feeds for import
Data import & catalog build
✓ Import products, collections, and content pages
✓ Set up metafields, filters, and search tools
✓ Migrate customer profiles and configure account invite flow
✓ Import historical orders for reference/reporting
Payments, shipping, tax
✓ Enable Shopify Payments and/or third-party gateways
✓ Configure domestic and international shipping rules
✓ Set up tax calculations for all regions
✓ Test payment flows and shipping scenarios
SEO & redirects
✓ Audit top URLs, keywords, and content
✓ Map and upload 301 redirects
✓ Migrate metadata and structured data
✓ Submit sitemap and monitor indexing
Design & UX
✓ Choose and customize theme
✓ Align page templates with performance and brand goals
✓ Optimize for mobile, accessibility, and load speed
✓ Enable editable content zones for marketing flexibility
Apps & integrations
✓ Review and rebuild all essential integrations
✓ Limit app usage to high-value tools
✓ Test data flow across all systems
✓ Document error handling and sync logic
Testing
✓ Run full QA across customer and admin flows
✓ Test tracking and analytics setup
✓ Validate behavior across regions, currencies, and devices
✓ Place real orders using different methods
Launch & post-launch
✓ Remove password protection and go live
✓ Confirm domain, redirects, and sitemap updates
✓ Monitor SEO performance, sales, and user behavior
✓ Support customer reactivation (passwords, saved data)
✓ Kick off CRO and performance optimization.
With the right preparation and a knowledgeable partner by your side, a Shopify migration becomes an opportunity to strengthen performance and create a store that supports growth.
At scandiweb, we’ve helped luxury retailers, marketplaces, and a range of ambitious brands with complex catalogs and global setups migrate to Shopify. If you’re planning a move to Shopify, we can help you avoid common risks during migration and set up a future-ready, customized store. Contact our Shopify expert team today to discuss your migration plan.


Share on: